UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| ☑ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2009
OR
| o | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15 (d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to .
Commission file no. 0-15886
THE NAVIGATORS GROUP, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | 13-3138397 (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
| 6 International Drive, Rye Brook, New York (Address of principal executive offices) | 10573 (Zip Code) |
Registrant's telephone number, including area code: (914) 934-8999
Securities registered pursuant to section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class: | Name of each exchange on which registered: | |
| Common Stock, $.10 Par Value | The NASDAQ Global Select Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes o No ☑
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No ☑
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☑ No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes o No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of the registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☑
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer", "accelerated filer" and "smaller reporting company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer o | Accelerated filer ☑ | Non-accelerated filer o | Smaller reporting company o |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes o No ☑
The aggregate market value of voting stock held by non-affiliates as of June 30, 2009 was $596,076,000
The number of common shares outstanding as of February 6, 2010 was 16,877,628.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the Company's 2010 Proxy Statement are incorporated by reference in Part III, Items 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14 of this Form 10-K.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| Description | Page Number | |||||||
| ||||||||
Note on Forward-Looking Statements | 3 | |||||||
| ||||||||
| PART I | ||||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 1. Business | 3 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Overview | 3 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Business Lines | 5 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Ratings | 8 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Loss Reserves | 9 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Catastrophe Risk Management | 15 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Hurricanes Gustav, Ike, Katrina and Rita | 16 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Reinsurance Recoverables | 17 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Investments | 19 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Regulation | 21 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Competition | 24 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Employees | 25 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Available Information | 25 | |||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 1A. Risk Factors | 26 | |||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments | 33 | |||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 2. Properties | 34 | |||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 3. Legal Proceedings | 34 | |||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 4. Submission of Matters to a Vote of Security Holders | 34 | |||||||
| ||||||||
| PART II | ||||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 5. Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities | 35 | |||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 6. Selected Financial Data | 39 | |||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | 40 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Overview | 40 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Critical Accounting Policies | 42 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Results of Operations | 51 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Segment Information | 70 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Off-Balance Sheet Transactions | 77 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Tabular Disclosure of Contractual Obligations | 77 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Investments | 78 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Liquidity and Capital Resources | 93 | |||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk | 98 | |||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data | 99 | |||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure | 99 | |||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 9A. Controls and Procedures | 99 | |||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 9B. Other Information | 102 | |||||||
| ||||||||
| PART III | ||||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance | 102 | |||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 11. Executive Compensation | 102 | |||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters | 102 | |||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence | 102 | |||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services | 103 | |||||||
| ||||||||
| PART IV | ||||||||
| ||||||||
ITEM 15. Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules | 103 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Signatures | 104 | |||||||
| ||||||||
Index to Consolidated Financial Statements and Schedules | F-1 | |||||||
| ||||||||
| Exhibit 11-1 | ||||||||
| Exhibit 21-1 | ||||||||
| Exhibit 23-1 | ||||||||
| Exhibit 31-1 | ||||||||
| Exhibit 31-2 | ||||||||
| Exhibit 32-1 | ||||||||
| Exhibit 32-2 | ||||||||
2
NOTE ON FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
Some of the statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K are "forward-looking statements" as defined in the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. All statements other than statements of historical fact included in or incorporated by reference in this Annual Report are forward-looking statements. Whenever used in this report, the words "estimate", "expect", "believe", "may", "will", "intend", "continue" or similar expressions or their negative are intended to identify such forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements are derived from information that we currently have and assumptions that we make. We cannot assure that anticipated results will be achieved, since actual results may differ materially because of both known and unknown risks and uncertainties which we face. Factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from our forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, the factors described in Part I, Item 1A, "Risk Factors" of this report. In light of these risks, uncertainties and assumptions, any forward-looking events discussed in this report may not occur. You are cautioned not to place undue reliance on any forward-looking statements, which speak only as of their respective dates. We undertake no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statement, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
The discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations contained herein should be read in conjunction with our Consolidated Financial Statements and accompanying notes which appear elsewhere in this report. They contain forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. Please see the above "Note on Forward-Looking Statements" for more information. Our actual results could differ materially from those anticipated in these forward-looking statements as a result of various factors, including those discussed above and elsewhere in this report.
Part I
Item 1. BUSINESS
Overview
The accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements, consisting of the accounts of The Navigators Group, Inc., a Delaware holding company established in 1982, and its wholly-owned subsidiaries, are prepared on the basis of U.S. generally accepted accounting principles ("GAAP" or "U.S. GAAP"). The preparation of these financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported revenues and expenses during the reporting periods along with related disclosures. The terms "we", "us", "our" and "the Company" as used herein are used to mean The Navigators Group, Inc. and its wholly-owned subsidiaries, unless the context otherwise requires. The terms "Parent" or "Parent Company" as used herein are used to mean The Navigators Group, Inc. without its subsidiaries.
We are an international insurance company focusing on specialty products within the overall property/casualty insurance market. Our largest product line and most long-standing area of specialization is ocean marine insurance. We have also developed specialty niches in professional liability insurance as well as other specialty insurance lines primarily consisting of contractors' liability and primary and excess liability coverages.
3
Our revenue is primarily comprised of premiums and investment income. We derive our premiums primarily from business written by wholly-owned underwriting management companies which produce, manage and underwrite insurance and reinsurance for us. Our products are distributed through multiple channels, utilizing global, national and regional retail and wholesale insurance brokers.
We conduct operations through our Insurance Companies and our Lloyd's Operations segments. The Insurance Companies segment consists of Navigators Insurance Company, which includes a United Kingdom Branch (the "U.K. Branch"), and Navigators Specialty Insurance Company, which underwrites specialty and professional liability insurance on an excess and surplus lines basis. All of the insurance business written by Navigators Specialty Insurance Company is fully reinsured by Navigators Insurance Company pursuant to a 100% quota share reinsurance agreement. Our Lloyd's Operations segment includes Navigators Underwriting Agency Ltd. ("NUAL"), a Lloyd's of London ("Lloyd's") underwriting agency which manages Lloyd's Syndicate 1221 ("Syndicate 1221"). Our Lloyd's Operations primarily underwrite marine and related lines of business along with offshore energy, professional liability insurance and construction coverages for onshore energy business at Lloyd's through Syndicate 1221. We controlled 100% of Syndicate 1221's stamp capacity for the 2009 and 2008 underwriting years through our wholly-owned subsidiary, Navigators Corporate Underwriters Ltd., and through both Millennium Underwriting Ltd., another wholly-owned subsidiary, and Navigators Corporate Underwriters Ltd. in 2007, which are referred to as corporate names in the Lloyd's market. We have also established underwriting agencies in Antwerp, Belgium, Stockholm, Sweden and Copenhagen, Denmark, which underwrite risks pursuant to binding authorities with NUAL into Syndicate 1221. For financial information by segment, see Note 3 to the Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 8 of this report.
During the 2008 second quarter, we closed two small underwriting agencies in Manchester and Basingstoke, England, which did not have a material effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
While management takes into consideration a wide range of factors in planning our business strategy and evaluating results of operations, there are certain factors that management believes are fundamental to understanding how we are managed. First, underwriting profit is consistently emphasized as a primary goal, above premium growth. Management's assessment of our trends and potential growth in underwriting profit is the dominant factor in its decisions with respect to whether or not to expand a business line, enter into a new niche, product or territory or, conversely, to contract capacity in any business line. In addition, management focuses on controlling the costs of our operations. Management believes that careful monitoring of the costs of existing operations and assessment of costs of potential growth opportunities are important to our profitability. Access to capital also has a significant impact on management's outlook for our operations. The Insurance Companies' operations and ability to grow their business and take advantage of market opportunities are constrained by regulatory capital requirements and rating agency assessments of capital adequacy. Similarly, the ability to grow our operations at Lloyd's is subject to Lloyd's capital and operating requirements.
Management's decisions are also greatly influenced by access to specialized underwriting and claims expertise in our lines of business. We have chosen to operate in specialty niches with certain common characteristics which we believe provide us with the opportunity to use our technical underwriting expertise in order to realize underwriting profit. As a result, we have focused on underserved markets for businesses characterized by higher severity and lower frequency of loss where we believe our intellectual capital and financial strength bring meaningful value. In contrast, we have avoided niches that we believe have a high frequency of loss activity and/or are subject to a high level of regulatory requirements, such as workers compensation and personal automobile insurance, because we do not believe our technical expertise is of as much value in these types of businesses. Examples of niches that have the characteristics we look for include bluewater hull which provides coverage for physical damage to, for example, highly valued cruise ships, and directors and officers liability ("D&O") insurance which covers litigation exposure of a corporation's directors and officers. These types of exposures require substantial technical expertise. We attempt to mitigate the financial impact of severe claims on our results by conservative and detailed underwriting, prudent use of reinsurance and a balanced portfolio of risks.
4
Business Lines
Effective in 2009, we reclassified certain business lines which had no effect on the segment classifications of the Insurance Companies and Lloyd's Operations. Underwriting data for prior periods has been reclassified to reflect these changes.
| • | The offshore energy business, formerly included in the "Marine and Energy" businesses of the Insurance Companies and Lloyd's Operations, is now included in the Insurance Companies' and Lloyd's Operations' "Property Casualty" businesses. |
| • | The marine lines within both the Insurance Companies and Lloyd's Operations are now presented as "Marine" instead of "Marine and Energy", since the offshore energy business has now been reclassified to "Property Casualty". |
| • | Engineering and construction, European Property and other run-off business, formerly included in the "Other" category of business within the Insurance Companies and Lloyd's Operations, are now included under "Property Casualty". |
| • | The "Middle Markets" business, formerly broken out separately in the Insurance Companies, is now included in the Insurance Companies' "Property Casualty" business. |
Marine
A summary of our business line divisions and primary products within those divisions, by operating segment, is as follows:
Marine - Insurance Companies | • Marine liability • Bluewater hull • Brownwater hull • Cargo, specie and logistics • Protection & indemnity • Transport • Builders risk • War • Customs bonds | |
| ||
Inland Marine - Insurance Companies | • Transportation • Construction equipment • Builders risk • Jewelry, fine arts & other specialties • Commercial output policy | |
| ||
Marine - Lloyd's Operations | • Cargo and specie • Marine liability • Bluewater hull • Marine excess-of-loss reinsurance |
5
Within the Insurance Companies' marine business, there are a number of different product lines. The largest is marine liability, which protects businesses from liability to third parties for bodily injury or property damage stemming from their marine-related operations, such as terminals, marinas and stevedoring. Another significant product line is bluewater hull, which provides coverage to the owners of ocean-going vessels against physical damage to the vessels. We also underwrite insurance for harbor craft and other small craft such as fishing vessels, providing physical damage and third party liability coverage. We underwrite cargo insurance, which provides coverage for physical damage to goods in the course of transit, whether by water, air or land. Our U.K. Branch also underwrites primary marine protection and indemnity ("P&I") business, which complements our marine liability business, which is generally written above the primary layer on an excess basis. In addition, we began to insure customs bonds in 2005. In 2006, we announced the establishment of an Inland Marine division of Navigators Insurance Company focusing on traditional inland marine insurance products including builders' risk, contractors' tools and equipment, fine arts, computer equipment and motor truck cargo.
Navigators Management Company, Inc., a wholly-owned underwriting agent, writes marine business for Navigators Insurance Company from offices located in major insurance or port locations in Chicago, Houston, London, Miami, New York, San Francisco and Seattle. Navigators Management UK Ltd., another wholly-owned underwriting agent, writes marine business in London for the UK Branch.
Prior to the 2006 underwriting year, Navigators Insurance Company obtained marine business through participation with other unaffiliated insurers in a marine insurance pool managed by our wholly-owned insurance agency subsidiaries. Commencing with the 2006 underwriting year, the marine insurance pool was eliminated and, therefore, all of the marine business generated by our underwriting agencies was exclusively for Navigators Insurance Company.
The largest product line within our Lloyd's Operations marine business is currently cargo. Other significant product lines include marine liability, specie, bluewater hull, and assumed reinsurance of other marine insurers on an excess-of-loss basis.
Property Casualty
A summary of our business line divisions and primary products within those divisions, by operating segment, is as follows. All of the Insurance Companies' business line divisions are divisions of Navigators Management Company, Inc.:
Navigators Property and Casualty (NAV PAC) - Insurance Companies | • Multi-Peril • Commercial automotive • Liability • Property • Umbrella • Inland marine • Crime insurance | |
| ||
Primary Casualty - Insurance Companies | • Construction liability • Construction wrap-up • Primary casualty • Environmental liability • Life sciences liability | |
| ||
Excess Casualty - Insurance Companies | • Excess casualty • Commercial umbrella | |
| ||
Navigators Technical Risk (NavTech) - Insurance Companies | • Offshore energy • Onshore energy • Operational engineering • Construction | |
| ||
Casualty - Lloyd's Operations | • Bloodstock • U.S. Casualty written through Lloyd's | |
| ||
Navigators Technical Risk (NavTech) - Lloyd's Operations | • Offshore energy • Onshore energy • Engineering and construction |
6
NAV PAC writes commercial multi-peril and commercial automobile insurance business for niche sectors such as adaptive driving firms, well drillers and armored cars. Our commercial multi-peril products include general liability and a small amount of property insurance. We do not underwrite workers compensation coverage. NAV PAC generally avoids writing property risks in areas with high exposure to earthquake or windstorm losses, such as California and Florida.
The Primary Casualty division primarily writes general liability insurance focusing on small general and artisan contractors and other targeted commercial risks. We have developed underwriting and claims expertise that we believe has allowed us to minimize our exposure to many of the large losses sustained in the past several years by other insurers, including losses stemming from coverages provided to larger contractors who work on condominiums, cooperative developments and other large housing developments. Consistent with our approach of emphasizing underwriting profit over market share, we direct our capacity to small to medium-size general contractors as well as artisan contractors. Commencing in 2005, we expanded our product line in this area by writing a limited number of construction wrap-up policies that are general liability policies for owners and developers of residential construction projects. In 2008, the Primary Casualty division diversified its industry focus and product capability to include products liability insurance to life sciences firms as well as environmental coverages, including liability insurance for contractors and environmental consultants and site pollution coverage.
The Excess Casualty division provides commercial umbrella and excess casualty insurance coverage. Areas of specialty include manufacturing and wholesale distribution, commercial construction, residential construction, construction project and wrap-up covers, business services, hospitality and real estate and niche programs.
In 2009, we reorganized our offshore energy, onshore energy, engineering and construction businesses under our NavTech division, which primarily underwrites through our Lloyd's Operations. Our engineering and construction business consists of coverage for construction projects including damage to machinery and equipment and loss of use due to delays. Our onshore and offshore energy insurance principally focuses on the oil and gas, chemical and petrochemical industries, with coverages primarily for property damage and business interruption.
The European property business, written by the Lloyd's Operations and the U.K. Branch beginning in 2006, was discontinued during the 2008 second quarter, which did not have any significant effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
7
Professional Liability
A summary of our business line divisions and products within those divisions, by operating segment, is as follows:
Navigators Professional Liability (Navigators Pro) - Insurance Companies | • Accountants professional liability • Directors & officers liability • Employment practice liability • Lawyers professional liability • Insurance agent errors & omissions • Miscellaneous professional liability | |
| ||
Navigators Professional Liability (Navigators Pro) - Lloyd's Operations | • Directors & officers liability • Lawyers professional liability |
Navigators Pro, a division of one of our wholly-owned insurance agencies, writes professional liability insurance. Our principal product in this division is directors and officers liability insurance, which we offer for both privately held and publicly traded corporations listed on national exchanges. In addition, we provide fiduciary liability and crime insurance to our directors and officers liability insurance clients.
Navigators Pro writes employment practices liability, lawyers professional liability and miscellaneous professional liability coverages. Our current target market for lawyers' professional liability is small law firms. Our U.K. Branch began writing professional liability coverages for U.K. solicitors in October 2004 and exited this business in 2007. In 2005, we commenced writing professional liability coverages for architects and engineers in our Insurance Companies and international directors and officers liability business in our Lloyd's Operations.
In September 2008, Syndicate 1221 began to underwrite professional and general liability insurance coverage in China through the Navigators Underwriting Division of Lloyd's Reinsurance Company (China) Ltd.
In October 2009, we opened an underwriting office in Copenhagen, Denmark to write professional and management liability business.
Ratings
Our ability to underwrite business is dependent upon the financial strength of the Insurance Companies and Lloyd's. Financial strength ratings represent the opinions of the rating agencies on the financial strength of a company and its capacity to meet the obligations of insurance policies. Independent ratings are one of the important factors that establish our competitive position in the insurance markets. The rating agencies consider many factors in determining the financial strength rating of an insurance company, including the relative level of statutory surplus necessary to support the business operations of the company. These ratings are based upon factors relevant to policyholders, agents and intermediaries and are not directed toward the protection of investors. Such ratings are not recommendations to buy, sell or hold securities. We could be adversely impacted by a downgrade in the Insurance Companies' or Lloyd's financial strength ratings, including a possible reduction in demand for our products, higher borrowing costs and our ability to access the capital markets.
8
For the Insurance Companies, Navigators Insurance Company and Navigators Specialty Insurance Company utilize the financial strength ratings from A.M. Best Company ("A.M. Best") and Standard and Poor's Rating Services ("S&P") for underwriting purposes. Navigators Insurance Company and Navigators Specialty Insurance Company are both rated "A" (Excellent - stable outlook) by A.M. Best and "A" (Strong - stable outlook) by S&P. Syndicate 1221 utilizes the ratings from A.M. Best and S&P for underwriting purposes which apply to all Lloyd's syndicates. Lloyd's is rated "A" (Excellent - stable outlook) by A.M. Best and A+ (Strong - stable outlook) by S&P.
Debt ratings apply to short-term and long-term debt as well as preferred stock. These ratings are assessments of the likelihood that we will make timely payments of the principal and interest for our senior debt. It is possible that, in the future, one or more of the rating agencies may reduce our existing debt ratings. If one or more of our debt ratings were downgraded, we could incur higher borrowing costs and our ability to access the capital markets could be impacted.
We utilize the senior debt ratings from S&P. Our senior debt is rated BBB (Adequate - stable outlook) by S&P.
Loss Reserves
We maintain reserves for unpaid losses and unpaid loss adjustment expenses for all lines of business. Loss reserves consist of both reserves for reported claims, known as case reserves, and reserves for losses that have occurred but have not yet been reported, known as incurred but not reported losses ("IBNR"). Case reserves are established when notice of a claim is first received. Reserves for such reported claims are established on a case-by-case basis by evaluating several factors, including the type of risk involved, knowledge of the circumstances surrounding such claim, severity of injury or damage, the potential for ultimate exposure, experience with the insured and the broker on the line of business, and the policy provisions relating to the type of claim. Reserves for IBNR are determined in part on the basis of statistical information and in part on the basis of industry experience. To the extent that reserves are deficient or redundant, the amount of such deficiency or redundancy is treated as a charge or credit to earnings in the period in which the deficiency or redundancy is identified. These reserves are intended to cover the probable ultimate cost of settling all losses incurred and unpaid, including those incurred but not reported. The determination of reserves for losses and loss adjustment expenses ("LAE") is dependent upon the receipt of information from insureds, brokers and agents.
Generally, there is a lag between the time premiums are written and related losses and loss adjustment expenses are incurred, and the time such events are reported to us. Our loss reserves include amounts related to short tail and long tail classes of business. Short tail business refers to claims that are generally reported quickly upon occurrence of an event, making estimation of loss reserves less complex. Our long tail business includes our marine liability, casualty and professional liability insurance products. For the long tail lines, significant periods of time, ranging up to several years or more, may elapse between the occurrence of the loss, the reporting of the loss and the settlement of the claim. Generally, the longer the time span between the incidence of a loss and the settlement of the claim, the more likely the ultimate settlement amount will vary from the original estimate. See the Casualty and Professional Liability section below for additional information.
9
Loss reserves are estimates of what the insurer or reinsurer expects to pay on claims, based on facts and circumstances then known. It is possible that the ultimate liability may exceed or be less than such estimates. In setting our loss reserve estimates, we review statistical data covering several years, analyze patterns by line of business and consider several factors including trends in claims frequency and severity, changes in operations, emerging economic and social trends, inflation and changes in the regulatory and litigation environment. Based on this review, we make a best estimate of our ultimate liability. We do not establish a range of loss estimates around the best estimate we use to establish our reserves and loss adjustment expenses. During the loss settlement period, which, in some cases, may last several years, additional facts regarding individual claims may become known and, accordingly, it often becomes necessary to refine and adjust the estimates of liability on a claim upward or downward. Such estimates are regularly reviewed and updated and any resulting adjustments are included in the current period's earnings. Even then, the ultimate liability may exceed or be less than the revised estimates. The reserving process is intended to provide implicit recognition of the impact of inflation and other factors affecting loss payments by taking into account changes in historical payment patterns and perceived probable trends. There is generally no precise method for the subsequent evaluation of the adequacy of the consideration given to inflation, or to any other specific factor, because the eventual deficiency or redundancy of reserves is affected by many factors, some of which are interdependent.
Another factor related to reserve development is that we record those premiums which are reported to us through the end of each calendar year and accrue estimates for premiums and loss reserves where there is a time lag between when the policy is bound and the recording of the policy. A substantial portion of the estimated premium is from international business where there can be significant time lags. To the extent that the actual premium varies from estimates, the difference, along with the related loss reserves and underwriting expenses, is recorded in current earnings.
As part of our risk management process, we purchase reinsurance to limit our liability on individual risks and to protect against catastrophic loss. We purchase both quota share reinsurance and excess-of-loss reinsurance. Quota share reinsurance is often utilized on the lower layers of risk and excess-of-loss reinsurance is used above the quota share reinsurance to limit our net retention per risk. Net retention represents the risk that we keep for our own account. Once our initial reserve is established and our net retention is exceeded, any adverse development will directly affect the gross loss reserve, but would generally have no impact on our net retained loss unless the aggregate limits available under the impacted excess-of-loss reinsurance treaty are exhausted. Generally, our limits of exposure are known with greater certainty when estimating our net loss versus our gross loss. This situation tends to create greater volatility in the deficiencies and redundancies of the gross reserves as compared to the net reserves.
10
The following table presents an analysis of losses and loss adjustment expenses for each of the last three calendar years:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net reserves for losses and LAE at beginning of year | $ | 999,871 | $ | 847,303 | $ | 696,116 | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
Provision for losses and LAE for claims occurring in the current year | 444,939 | 443,877 | 387,601 | |||||||||
Decrease in estimated losses and LAE for claims occurring in prior years | (8,941 | ) | (50,746 | ) | (47,009 | ) | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
Incurred losses and LAE | 435,998 | 393,131 | 340,592 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Losses and LAE paid for claims occurring during: | ||||||||||||
Current year | (59,412 | ) | (60,104 | ) | (46,467 | ) | ||||||
Prior years | (263,523 | ) | (180,459 | ) | (142,938 | ) | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
Losses and LAE payments | (322,935 | ) | (240,563 | ) | (189,405 | ) | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net reserves for losses and LAE at end of year | 1,112,934 | 999,871 | 847,303 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Reinsurance recoverables on unpaid losses and LAE | 807,352 | 853,793 | 801,461 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Gross reserves for losses and LAE at end of year | $ | 1,920,286 | $ | 1,853,664 | $ | 1,648,764 | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
The following table presents the development of the loss and LAE reserves for 1999 through 2009. The line "Net reserves for losses and LAE" reflects the net reserves at the balance sheet date for each of the indicated years and represents the estimated amount of losses and loss adjustment expenses arising in all prior years that are unpaid at the balance sheet date. The "Reserves for losses and LAE re-estimated" lines of the table reflect the re-estimated amount of the previously recorded reserves based on experience as of the end of each succeeding year. The reserve estimates may change as more information becomes known about the frequency and severity of claims for individual years. The net and gross cumulative redundancy (deficiency) lines of the table reflect the cumulative amounts developed as of successive years with respect to the aforementioned reserve liability. The cumulative redundancy or deficiency represents the aggregate change in the estimates over all prior years.
The table allocates losses and loss adjustment expenses reported and recorded in subsequent years to all prior years starting with the year in which the loss was incurred. For example, assuming that a loss occurred in 2000 and was not reported until 2002, the amount of such loss will appear as a deficiency in both 2000 and 2001. Conditions and trends that have affected development of the liability in the past may not necessarily occur in the future. Accordingly, it may not be appropriate to extrapolate future redundancies or deficiencies based on the table.
11
The favorable or adverse development on our gross reserves has mostly been ceded to our excess-of-loss reinsurance treaties. As a result of these reinsurance arrangements, while our gross losses and related reserve deficiencies and redundancies are very sensitive to favorable or adverse developments such as those described above, our net losses and related reserve deficiencies and redundancies tend to be less sensitive to such developments.
Our gross loss reserves include estimated losses related to the 2005 Hurricanes Katrina and Rita and the 2008 Hurricanes Ike and Gustav and were in total approximately 6.6% of the total December 31, 2009 gross loss reserves and 11.1% of the total December 31, 2008 gross loss reserves. In addition, our gross loss reserves include estimated losses related to our historic asbestos exposure and were approximately 1.2% of the total December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008 gross loss reserves, respectively. When recording these losses, we assess our reinsurance coverage, potential reinsurance recoverable, and the recoverability of those balances.
Losses incurred on business recently written are primarily covered by reinsurance agreements written by companies with whom we are currently doing reinsurance business and whose credit we continue to assess in the normal course of business. See "Management's Discussion of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Results of Operations - Operating Expenses - Net Losses and Loss Adjustment Expenses Incurred" and Note 5 - Loss Reserves for Losses and Loss Adjustment Expenses in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, both of which are included herein, for additional information regarding Hurricanes Katrina, Rita, Ike and Gustav and our asbestos exposure.
12
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net reserves for losses and LAE | $ | 170,530 | $ | 174,883 | $ | 202,759 | $ | 264,647 | $ | 374,171 | $ | 463,788 | $ | 578,976 | $ | 696,116 | $ | 847,303 | $ | 999,871 | $ | 1,112,934 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Reserves for losses and LAE re-estimated as of: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
One year later | 165,536 | 180,268 | 209,797 | 323,282 | 370,335 | 460,007 | 561,762 | 649,107 | 796,557 | 990,930 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Two years later | 160,096 | 183,344 | 266,459 | 328,683 | 360,964 | 457,769 | 523,541 | 589,044 | 776,844 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Three years later | 156,322 | 232,530 | 266,097 | 321,213 | 377,229 | 432,988 | 481,532 | 555,448 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Four years later | 194,924 | 227,554 | 256,236 | 334,991 | 362,227 | 401,380 | 461,563 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Five years later | 190,830 | 218,982 | 264,431 | 325,249 | 343,182 | 391,766 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Six years later | 185,075 | 225,031 | 260,264 | 314,332 | 333,857 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Seven years later | 188,055 | 221,541 | 257,852 | 305,051 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Eight years later | 187,422 | 220,045 | 250,021 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nine years later | 186,581 | 213,198 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ten years later | 180,431 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net cumulative redundancy (deficiency) | (9,901 | ) | (38,315 | ) | (47,262 | ) | (40,404 | ) | 40,314 | 72,022 | 117,413 | 140,668 | 70,458 | 8,941 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net cumulative paid as of: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
One year later | 43,301 | 53,646 | 64,785 | 84,385 | 80,034 | 96,981 | 133,337 | 142,938 | 180,459 | 263,523 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Two years later | 71,535 | 91,352 | 112,746 | 133,911 | 140,644 | 180,121 | 219,125 | 233,211 | 322,892 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Three years later | 88,570 | 114,449 | 138,086 | 170,236 | 195,961 | 238,673 | 264,663 | 300,328 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Four years later | 101,667 | 127,961 | 159,042 | 208,266 | 223,847 | 262,425 | 302,273 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Five years later | 108,146 | 141,384 | 185,037 | 226,798 | 239,355 | 283,538 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Six years later | 116,752 | 159,389 | 196,098 | 234,284 | 251,006 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Seven years later | 131,579 | 171,768 | 198,760 | 241,083 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Eight years later | 142,709 | 171,744 | 203,370 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nine years later | 142,101 | 176,876 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ten years later | 146,798 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gross liability-end of year | 391,094 | 357,674 | 401,177 | 489,642 | 724,612 | 966,117 | 1,557,991 | 1,607,555 | 1,648,764 | 1,853,664 | 1,920,286 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reinsurance recoverable | 220,564 | 182,791 | 198,418 | 224,995 | 350,441 | 502,329 | 979,015 | 911,439 | 801,461 | 853,793 | 807,352 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net liability-end of year | 170,530 | 174,883 | 202,759 | 264,647 | 374,171 | 463,788 | 578,976 | 696,116 | 847,303 | 999,871 | 1,112,934 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gross re-estimated latest | 429,719 | 463,960 | 529,707 | 639,674 | 698,021 | 862,260 | 1,367,835 | 1,388,088 | 1,544,672 | 1,851,667 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Re-estimated recoverable latest | 249,289 | 250,763 | 279,685 | 334,623 | 364,164 | 470,493 | 906,272 | 832,640 | 767,828 | 860,737 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net re-estimated latest | 180,431 | 213,198 | 250,021 | 305,051 | 333,857 | 391,766 | 461,563 | 555,448 | 776,844 | 990,930 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gross cumulative redundancy (deficiency) | (38,625 | ) | (106,286 | ) | (128,530 | ) | (150,032 | ) | 26,591 | 103,857 | 190,156 | 219,467 | 104,092 | 1,997 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
13
The following tables identify the approximate gross and net cumulative redundancy (deficiency) at each year-end balance sheet date for the Insurance Companies and Lloyd's Operations contained in the preceding ten year table:
Gross Cumulative Redundancy (Deficiency)
| Consolidated | Insurance Companies | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year | Grand | Excluding | All | Lloyd's | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ended | Total | Asbestos | Total | Asbestos | Other (1) | Operations | ||||||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
2008 | $ | 1,997 | $ | 2,926 | $ | (16,517 | ) | $ | (929 | ) | $ | (15,588 | ) | $ | 18,514 | |||||||||
2007 | 104,092 | 105,817 | 57,512 | (1,725 | ) | 59,237 | 46,580 | |||||||||||||||||
2006 | 219,467 | 220,412 | 131,443 | (945 | ) | 132,388 | 88,024 | |||||||||||||||||
2005 | 190,156 | 191,347 | 97,758 | (1,191 | ) | 98,949 | 92,398 | |||||||||||||||||
2004 | 103,857 | 87,639 | 84,639 | 16,218 | 68,421 | 19,218 | ||||||||||||||||||
2003 | 26,591 | 11,556 | 20,128 | 15,035 | 5,093 | 6,463 | ||||||||||||||||||
2002 | (150,032 | ) | (87,230 | ) | (144,804 | ) | (62,802 | ) | (82,002 | ) | (5,228 | ) | ||||||||||||
2001 | (128,530 | ) | (65,371 | ) | (117,136 | ) | (63,159 | ) | (53,977 | ) | (11,394 | ) | ||||||||||||
2000 | (106,286 | ) | (42,879 | ) | (77,340 | ) | (63,407 | ) | (13,933 | ) | (28,946 | ) | ||||||||||||
1999 | (38,625 | ) | 24,893 | (21,912 | ) | (63,518 | ) | 41,606 | (16,713 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Net Cumulative Redundancy (Deficiency)
| Consolidated | Insurance Companies | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year | Grand | Excluding | All | Lloyd's | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ended | Total | Asbestos | Total | Asbestos | Other (1) | Operations | ||||||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
2008 | $ | 8,941 | $ | 8,916 | $ | 3,079 | $ | 25 | $ | 3,054 | $ | 5,862 | ||||||||||||
2007 | 70,458 | 70,696 | 54,475 | (238 | ) | 54,713 | 15,983 | |||||||||||||||||
2006 | 140,668 | 142,685 | 104,831 | (2,017 | ) | 106,848 | 35,837 | |||||||||||||||||
2005 | 117,413 | 119,659 | 85,408 | (2,246 | ) | 87,654 | 32,005 | |||||||||||||||||
2004 | 72,022 | 74,797 | 51,083 | (2,775 | ) | 53,858 | 20,939 | |||||||||||||||||
2003 | 40,314 | 43,494 | 19,279 | (3,180 | ) | 22,459 | 21,035 | |||||||||||||||||
2002 | (40,404 | ) | (5,544 | ) | (51,720 | ) | (34,860 | ) | (16,860 | ) | 11,316 | |||||||||||||
2001 | (47,262 | ) | (12,254 | ) | (47,261 | ) | (35,008 | ) | (12,253 | ) | (1 | ) | ||||||||||||
2000 | (38,315 | ) | (3,213 | ) | (28,001 | ) | (35,102 | ) | 7,101 | (10,314 | ) | |||||||||||||
1999 | (9,901 | ) | 25,306 | (6,730 | ) | (35,207 | ) | 28,477 | (3,171 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| (1) | Contains cumulative loss development for all active and run-off lines of business exclusive of asbestos losses. |
14
Casualty and Professional Liability. Substantially all of our casualty business involves general liability policies which generate third party liability claims that are long tail in nature. A significant portion of our general liability reserves relate to construction defect claims. Reserves and claim frequency on this business may be impacted by legislation implemented in California, which generally provides consumers who experience construction defects a method other than litigation to obtain construction defect repairs. The law, which became effective July 1, 2002 with a sunset provision effective January 1, 2011, provides for an alternative dispute resolution system that attempts to involve all parties to the claim at an early stage. This legislation may impact claim severity, frequency and length of settlement assumptions underlying our reserves. Accordingly, our ultimate liability may exceed or be less than current estimates due to this variable, among others.
The professional liability business generates third party claims, which also are longer tail in nature. The professional liability policies mainly provide coverage on a claims-made basis, whereby coverage is generally provided only for those claims that are made during the policy period. The substantial majority of our claims-made policies provide coverage for one year periods. We have also issued a limited number of multi-year claims-made professional liability policies known as "tail coverage" that provide for insurance protection for wrongful acts prior to the run-off date. Such multi-year policies provide insurance protection for several years.
Loss development of our professional liability business is relatively immature, as we first began writing the business in late 2001. Accordingly, it will take some time to better understand the reserve trends on this business. Our professional liability loss estimates are based on expected losses, actual reported losses, evaluation of loss trends, industry data, and the legal, regulatory and current risk environment because anticipated loss experience in this area is less predictable due to the small number of claims and/or erratic claim severity patterns. We believe that we have made a reasonable estimate of the required loss reserves for professional liability. The expected ultimate losses may be adjusted up or down as the accident years mature.
Additional information regarding our loss and loss adjustment expenses incurred and loss reserves can be found in "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Results of Operations - Operating Expenses - Net Losses and Loss Adjustment Expenses Incurred" and Note 5, Reserves for Losses and Loss Adjustment Expenses , in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, both of which are included herein.
Catastrophe Risk Management
We have exposure to losses caused by hurricanes and other natural and man-made catastrophic events. The frequency and severity of catastrophes are unpredictable.
The extent of losses from a catastrophe is a function of both the total amount of insured exposure in an area affected by the event and the severity of the event. We continually assess our concentration of underwriting exposures in catastrophe exposed areas globally and attempt to manage this exposure through individual risk selection and through the purchase of reinsurance. We also use modeling and concentration management tools that allow us to better monitor and control our accumulations of potential losses from catastrophe exposures. Despite these efforts, there remains uncertainty about the characteristics, timing and extent of insured losses given the nature of catastrophes. The occurrence of one or more severe catastrophic events could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition and/or liquidity.
We have significant natural catastrophe exposures throughout the world. Historically our largest natural catastrophe exposure emanated from offshore energy platforms exposed to hurricanes in the Gulf of Mexico. In 2009 we reduced our exposure to that peril. The majority of the offshore energy policies that have historically exposed us to this peril renew in the second and third quarters of the year. During the third quarter of 2009, we found the available market pricing and policy terms to be unacceptable in most cases and, therefore, offered coverage for the peril of windstorm in the Gulf of Mexico on only a very small number of risks. Accordingly, our current exposure to hurricanes in the Gulf of Mexico is materially less than what it was one year ago, and it therefore no longer represents our largest natural catastrophe exposure.
15
We estimate that our largest exposure to loss from a single natural catastrophe event now comes from an earthquake on the west coast of the United States. As of January 1, 2010, we estimate that our probable maximum pre-tax gross and net loss exposure for an earthquake event centered at San Francisco, California would be approximately $127 million and $27 million, respectively, including the cost of reinsurance reinstatement premiums.
Like all catastrophe exposure estimates, the foregoing estimate of our probable maximum loss is inherently uncertain. This estimate is highly dependent upon numerous assumptions and subjective underwriting judgments. Examples of significant assumptions and judgments related to such an estimate include the intensity, depth and location of the earthquake, the various types of the insured risks exposed to the event at the time the event occurs and the estimated costs or damages incurred for each insured risk. The composition of our portfolio also makes such estimates challenging due to the non-static nature of the exposures covered under our policies in lines of business such as cargo and hull. There can be no assurances that the gross and net loss amounts that we could incur in such an event or in any natural catastrophe event would not be materially higher than the estimates discussed above given the significant uncertainties with respect to such an estimate. Moreover, our portfolio of insured risks changes dynamically over time and there can be no assurance that our probable maximum loss will not change materially over time.
The occurrence of large loss events could reduce the reinsurance coverage that is available to us and could weaken the financial condition of our reinsurers, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations. Although the reinsurance agreements make the reinsurers liable to us to the extent the risk is transferred or ceded to the reinsurer, ceded reinsurance arrangements do not eliminate our obligation to pay claims to our policyholders as we are required to pay the losses if a reinsurer fails to meet its obligations under the reinsurance agreement. Accordingly, we bear credit risk with respect to our reinsurers. Specifically, our reinsurers may not pay claims made by us on a timely basis, or they may not pay some or all of these claims. Either of these events would increase our costs and could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Hurricanes Gustav, Ike, Katrina and Rita
Hurricanes Gustav and Ike (the "2008 Hurricanes") which occurred in the 2008 third quarter and Hurricanes Katrina and Rita (the "2005 Hurricanes") which occurred in the 2005 third quarter generated substantial losses in our marine and energy lines of business, due principally to offshore energy losses. There were no significant hurricane losses in 2009, 2007 or 2006 that impacted our marine and energy lines of business.
We monitor the development of paid and reported claims activities in relation to the estimate of ultimate losses established for the 2008 Hurricanes and the 2005 Hurricanes. Management believes that should any adverse loss development for gross claims occur from the 2008 Hurricanes or the 2005 Hurricanes, it would be contained within our reinsurance program. Our actual losses from such hurricanes may differ materially from our estimated losses as a result of, among other things, the receipt of additional information from insureds or brokers, the attribution of losses to coverages that, for the purposes of our estimates, we assumed would not be exposed and inflation in repair costs due to the limited availability of labor and materials. If our actual losses from the 2008 Hurricanes or the 2005 Hurricanes are materially greater than our estimated losses, our business, results of operations and financial condition could be materially adversely affected.
16
See "Management's Discussion of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Results of Operations and Overview - Operating Expenses - Net Losses and Loss Adjustment Expenses Incurred" and Note 5 - Loss Reserves for Losses and Loss Adjustment Expenses in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, both of which are included herein, for additional information regarding Hurricanes Katrina, Rita, Ike and Gustav.
Reinsurance Recoverables
We utilize reinsurance principally to reduce our exposure on individual risks, to protect against catastrophic losses and to stabilize loss ratios and underwriting results. We are protected by various treaty and facultative reinsurance agreements. The reinsurance is placed either directly by us or through reinsurance intermediaries. The reinsurance intermediaries are compensated by the reinsurers.
Although reinsurance makes the reinsurer liable to us to the extent the risk is transferred or ceded to the reinsurer, ceded reinsurance arrangements do not eliminate our obligation to pay claims to our policyholders. Accordingly, we bear credit risk with respect to our reinsurers. Specifically, our reinsurers may not pay claims made by us on a timely basis, or they may not pay some or all of these claims. Either of these events would increase our costs and could have a material adverse effect on our business. Losses we incurred due to Hurricanes Katrina and Rita in 2005 and Hurricanes Gustav and Ike in 2008 significantly increased our reinsurance recoverables, resulting in an increase to our credit risk exposure to our reinsurers.
We have established a reserve for uncollectible reinsurance in the amount of $13.8 million, which was determined by considering reinsurer specific default risk as indicated by their financial strength ratings.
Our exposure to credit risk from any one reinsurer is managed through diversification by reinsuring with a number of different reinsurers, principally in the United States and European reinsurance markets. When reinsurance is placed, our standards of acceptability generally require that a reinsurer must have a rating from A.M. Best and/or S&P of "A" or better, or an equivalent financial strength if not rated, plus at least $250 million in policyholders' surplus. Our Reinsurance Security Committee, which is included within our Enterprise Risk Management Finance and Credit Sub-Committee, monitors the financial strength of our reinsurers and the related reinsurance recoverables and periodically reviews the list of acceptable reinsurers.
The credit quality distribution of the Company's reinsurance recoverables of $1.05 billion at December 31, 2009 for ceded paid and unpaid losses and loss adjustment expenses and ceded unearned premiums based on insurer financial strength ratings from A.M. Best was as follows:
| A.M. Best | Rating | Recoverable | Percent | |||||||
| Rating (1) | Description | Amounts | of Total | |||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||
A++, A+ | Superior | $ | 436.7 | 42 | % | |||||
A, A- | Excellent | 585.2 | 56 | % | ||||||
B++, B+ | Very good | 0.8 | 0 | % (2) | ||||||
NR | Not rated | 23.5 | 2 | % (2) | ||||||
| ||||||||||
Total | $ | 1,046.2 | 100 | % | ||||||
| ||||||||||
| (1) | Equivalent S&P rating used for certain companies when an A.M. Best rating was unavailable. | |
| (2) | The Company holds offsetting collateral of approximately 102.1% for B++ and B+ companies and 71.8% for not rated companies which includes letters of credit, ceded balances payable and other balances held by our Insurance Companies and our Lloyd's Operations. |
17
The following table lists our 20 largest reinsurers measured by the amount of reinsurance recoverable for ceded paid and unpaid losses and loss adjustment expense and ceded unearned premium (constituting 75.6% of our total recoverables) together with the collateral held by us at December 31, 2009, and the reinsurers' financial strength rating from the indicated rating agency:
| Reinsurance Recoverables | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Unearned | Unpaid/Paid | Collateral | Rating & | ||||||||||||||||||
| Reinsurer | Premium | Losses | Total | Held (1) | Rating Agency | ||||||||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Swiss Reinsurance America Corporation | $ | 9.0 | $ | 97.8 | $ | 106.8 | $ | 9.2 | A | AMB | (2) | ||||||||||
Munich Reinsurance America Inc. | 26.1 | 60.3 | 86.4 | 16.2 | A+ | AMB | |||||||||||||||
Transatlantic Reinsurance Company | 21.7 | 49.3 | 71.0 | 9.5 | A | AMB | |||||||||||||||
White Mountains Reinsurance of America | 1.2 | 68.6 | 69.8 | 2.3 | A- | AMB | |||||||||||||||
Everest Reinsurance Company | 19.9 | 49.4 | 69.3 | 8.5 | A+ | AMB | |||||||||||||||
General Reinsurance Corporation | 1.5 | 58.3 | 59.8 | 1.7 | A++ | AMB | |||||||||||||||
Munchener Ruckversicherungs-Gesellschaft | 4.9 | 37.0 | 41.9 | 10.2 | A+ | AMB | |||||||||||||||
National Indemnity Company | 7.5 | 29.8 | 37.3 | 3.1 | A++ | AMB | |||||||||||||||
Platinum Underwriters Re | 4.2 | 26.8 | 31.0 | 2.6 | A | AMB | |||||||||||||||
Berkley Insurance Company | 8.1 | 21.1 | 29.2 | 1.5 | A+ | AMB | |||||||||||||||
Scor Holding (Switzerland) AG | 5.9 | 19.2 | 25.1 | 5.9 | A- | AMB | |||||||||||||||
Swiss Re International SE | 1.3 | 22.2 | 23.5 | 6.2 | A | AMB | |||||||||||||||
Partner Reinsurance Europe | 5.6 | 17.6 | 23.2 | 8.7 | AA- | S&P | |||||||||||||||
Lloyd's Syndicate #2003 | 3.6 | 17.9 | 21.5 | 3.4 | A | AMB | |||||||||||||||
Partner Reinsurance Company of the U.S. | 1.0 | 19.6 | 20.6 | 0.1 | A+ | AMB | |||||||||||||||
Arch Reinsurance Company | 0.7 | 15.9 | 16.6 | 0.1 | A | AMB | |||||||||||||||
Hannover Ruckversicherung | 1.5 | 14.8 | 16.3 | 2.4 | A | AMB | |||||||||||||||
Ace Property and Casualty Insurance Company | 3.7 | 12.1 | 15.8 | 1.6 | A+ | AMB | |||||||||||||||
Allianz Global Corporate & Specialty AG | 0.2 | 14.4 | 14.6 | 4.2 | A+ | AMB | |||||||||||||||
Federal Insurance Co. | 0.6 | 10.7 | 11.3 | 1.0 | A++ | AMB | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Top 20 Total | 128.2 | 662.8 | 791.0 | 98.4 | |||||||||||||||||
All Other | 34.1 | 221.1 | 255.2 | 80.9 | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 162.3 | $ | 883.9 | $ | 1,046.2 | $ | 179.3 | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Collateral includes letters of credit, ceded balances payable and other balances held by our Insurance Companies and our Lloyd's Operations. | |
| (2) | A.M. Best |
The largest portion of the collateral held consists of letters of credit obtained from reinsurers in accordance with New York Insurance Department Regulation No. 133. Such regulation requires collateral to be held by the ceding company from reinsurers not licensed in New York State in order for the ceding company to take credit for the reinsurance recoverables on its statutory balance sheet. The specific requirements governing the letters of credit include a clean and unconditional letter of credit and an "evergreen" clause which prevents the expiration of the letter of credit without due notice to the Company. Only banks considered qualified by the National Association of Insurance Commissioners ("NAIC") may be deemed acceptable issuers of letters of credit by the New York Insurance Department. In addition, based on our credit assessment of the reinsurer, there are certain instances where we require collateral from a reinsurer even if the reinsurer is licensed in New York State, generally applying the requirements of Regulation No. 133. The contractual terms of the letters of credit require that access to the collateral is unrestricted. In the event that the counterparty to our collateral would be deemed not qualified by the NAIC, the reinsurer would be required by agreement to replace such collateral with acceptable security under the reinsurance agreement. There is no assurance, however, that the reinsurer would be able to replace the counterparty bank in the event such counterparty bank becomes unqualified and the reinsurer experiences significant financial deterioration. Under such circumstances, we could incur a substantial loss from uncollectible reinsurance from such reinsurer.
18
Approximately $69.7 million and $96.8 million of the reinsurance recoverables for paid and unpaid losses at December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008, respectively, were due from reinsurers as a result of the losses from the 2008 Hurricanes Gustav and Ike. Approximately $68.5 million and $101.7 million of the reinsurance recoverables for paid and unpaid losses at December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively, were due from reinsurers as a result of the losses from the 2005 Hurricanes Katrina and Rita. In addition, also included in reinsurance recoverable for paid and unpaid losses were approximately $8.9 million at both December 31, 2009 and 2008 due from reinsurers in connection with our asbestos exposures.
See "Business - Regulation - United States" below for information regarding the Terrorism Risk Insurance Act, the Terrorism Risk Insurance Extension Act and the Terrorism Risk Insurance Program Reauthorization Act.
Investments
The objective of our investment policy, guidelines and strategy is to maximize total investment return in the context of preserving and enhancing shareholder value and statutory surplus of the Insurance Companies. Secondarily, we seek to optimize after-tax investment income.
Our investments are managed by outside professional fixed-income and equity portfolio managers. We seek to achieve our investment objectives by investing in cash equivalents and money market funds, municipal bonds, U.S. Government bonds, U.S. Government agency guaranteed and non-guaranteed securities, corporate bonds, mortgage-backed and asset-backed securities and common and preferred stocks.
Our investment guidelines require that the amount of our consolidated fixed-income portfolio rated below "A-" but no lower than "BBB-" by S&P or below "A3" but no lower than "Baa3" by Moody's Investors Service ("Moody's") shall not exceed 10% of our total fixed income and short-term investments. Fixed-income securities rated below "BBB-" by S&P or "Baa3" by Moody's combined with any other investments not specifically permitted under our investment guidelines, cannot exceed 5% of our consolidated stockholders' equity. Investments in equity securities that are actively traded on major U.S. stock exchanges cannot exceed 20% of consolidated stockholders' equity. Finally, our investment guidelines prohibit investments in derivatives other than as a hedge against foreign currency exposures or the writing of covered call options on our equity portfolio.
The Insurance Companies' investments are subject to the oversight of their respective Boards of Directors and our Finance Committee of the Parent Company's Board of Directors. The investment portfolio and the performance of the investment managers are reviewed quarterly. These investments must comply with the insurance laws of New York State, the domiciliary state of Navigators Insurance Company and Navigators Specialty Insurance Company. These laws prescribe the type, quality and concentration of investments which may be made by insurance companies. In general, these laws permit investments, within specified limits and subject to certain qualifications, in federal, state and municipal obligations, corporate bonds, preferred stocks, common stocks, real estate mortgages and real estate. The U.K. Branch's investments must comply with the regulations set forth by the Financial Services Authority ("FSA") in the U.K.
19
The Lloyd's Operations' investments are subject to the direction and control of the Board of Directors and the Investment and Capital Committee of NUAL, as well as the Parent Company's Board of Directors and Finance Committee. These investments must comply with the rules and regulations imposed by Lloyd's and the FSA.
The table set forth below reflects our total investment balances, net investment income earned thereon and the related average yield for the last three calendar years:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||
Invested Assets and Cash | ||||||||||||
Insurance Companies | $ | 1,604,354 | $ | 1,509,382 | $ | 1,421,365 | ||||||
Lloyd's Operations | 388,556 | 356,184 | 301,790 | |||||||||
Parent Company | 63,677 | 52,149 | 44,146 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Consolidated | $ | 2,056,587 | $ | 1,917,715 | $ | 1,767,301 | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net Investment Income | ||||||||||||
Insurance Companies | $ | 65,717 | $ | 63,544 | $ | 58,261 | ||||||
Lloyd's Operations | 9,229 | 11,655 | 10,524 | |||||||||
Parent Company | 566 | 1,355 | 1,877 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Consolidated | $ | 75,512 | $ | 76,554 | $ | 70,662 | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Average Yield (amortized cost basis) | ||||||||||||
Insurance Companies | 4.1 | % | 4.3 | % | 4.5 | % | ||||||
Lloyd's Operations | 2.7 | % | 3.4 | % | 3.9 | % | ||||||
Parent Company | 1.0 | % | 3.1 | % | 4.9 | % | ||||||
Consolidated | 3.8 | % | 4.1 | % | 4.4 | % | ||||||
At December 31, 2009, the average quality of the investment portfolio was rated "AA" by S&P and "Aa" by Moody's. All of the Company's mortgage-backed and asset-backed securities were rated "AAA" by S&P and "Aaa" by Moody's except for 77 securities approximating $59.9 million. There were no collateralized debt obligations (CDO's), collateralized loan obligations (CLO's), asset-backed commercial paper or credit default swaps in our investment portfolio. At December 31, 2009 and 2008, all fixed-maturity and equity securities held by us were classified as available-for-sale.
See "Management's Discussion of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Investments" and Note 4 - Investments in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, both of which are included herein, for additional information regarding investments.
20
Regulation
United States
We are subject to regulation under the insurance statutes, including holding company statutes, of various states and applicable regulatory authorities in the United States. These regulations vary but generally require insurance holding companies, and insurers that are subsidiaries of holding companies, to register and file reports concerning their capital structure, ownership, financial condition and general business operations. Such regulations also generally require prior regulatory agency approval of changes in control of an insurer and of transactions within the holding company structure. The regulatory agencies have statutory authorization to enforce their laws and regulations through various administrative orders and enforcement proceedings.
Navigators Insurance Company is licensed to engage in the insurance and reinsurance business in 50 states, the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico. Navigators Specialty Insurance Company is licensed to engage in the insurance and reinsurance business in the State of New York and is an approved surplus lines insurer or meets the financial requirements where there is not a formal approval process in all other states and the District of Columbia.
The State of New York Insurance Department is our principal regulatory agency. New York insurance law provides that no corporation or other person may acquire control of us, and thus indirect control of our insurance company subsidiaries, unless it has given notice to our insurance company subsidiaries and obtained prior written approval from the Superintendent of Insurance of the State of New York for such acquisition. Any purchaser of 10% or more of the outstanding shares of our common stock would be presumed to have acquired control of us, unless such presumption is rebutted.
Under New York insurance law, Navigators Insurance Company and Navigators Specialty Insurance Company may only pay dividends out of their statutory earned surplus. Generally, the maximum amount of dividends Navigators Insurance Company and Navigators Specialty Insurance Company may pay without regulatory approval in any twelve-month period is the lesser of adjusted net investment income or 10% of statutory surplus. For a discussion of our current dividend capacity, see "Management's Discussion of Financial Condition and Results of Operations-Liquidity and Capital Resources" in Item 7 of this report.
As part of its general regulatory oversight process, the New York Insurance Department conducts detailed examinations of the books, records and accounts of New York insurance companies every three to five years. Navigators Insurance Company and Navigators Specialty Insurance Company were examined for the years 2001 through 2004 by the New York Insurance Department. The New York Insurance Department commenced an examination of the years 2005 through 2009 in January 2010.
Under insolvency or guaranty laws in most states in which Navigators Insurance Company and Navigators Specialty Insurance Company operate, insurers doing business in those states can be assessed up to prescribed limits for policyholder losses of insolvent insurance companies. Neither Navigators Insurance Company nor Navigators Specialty Insurance Company was subject to any material assessments under state insolvency or guaranty laws in the last three years.
21
The Insurance Regulatory Information System, or IRIS, was developed by the NAIC and is intended primarily to assist state insurance departments in executing their statutory mandates to oversee the financial condition of insurance companies operating in their respective states. IRIS identifies thirteen industry ratios and specifies "usual values" for each ratio. Departure from the usual values on four or more of the ratios can lead to inquiries from individual state insurance commissioners as to certain aspects of an insurer's business. As of December 31, 2009, the results for both Navigators Insurance Company and Navigators Specialty Insurance Company were within the usual values for all IRIS ratios.
State insurance departments have adopted a methodology developed by the NAIC for assessing the adequacy of statutory surplus of property and casualty insurers which includes a risk-based capital formula that attempts to measure statutory capital and surplus needs based on the risks in a company's mix of products and investment portfolio. The formula is designed to allow state insurance regulators to identify weakly capitalized companies. Under the formula, a company determines its "risk-based capital" by taking into account certain risks related to the insurer's assets (including risks related to its investment portfolio and ceded reinsurance) and the insurer's liabilities (including underwriting risks related to the nature and experience of its insurance business). The risk-based capital rules provide for different levels of regulatory attention depending on the ratio of a company's total adjusted capital to its "authorized control level" of risk-based capital. Based on calculations made by Navigators Insurance Company and Navigators Specialty Insurance Company, their risk-based capital levels exceed the level that would trigger regulatory attention or company action. In their respective 2008 statutory financial statements, Navigators Insurance Company and Navigators Specialty Insurance Company have complied with the NAIC's risk-based capital reporting requirements.
In addition to regulations applicable to insurance agents generally, Navigators Management Company, Inc. is subject to managing general agents' acts in its state of domicile and in certain other jurisdictions where it does business.
In 2002, in response to the tightening of supply in certain insurance and reinsurance markets resulting from, among other things, the September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks, the Terrorism Risk Insurance Act, or TRIA, was enacted. TRIA was intended to ensure the availability of insurance coverage for "acts of terrorism" (as defined) in the United States of America committed by or on behalf of foreign persons or interests. This law established a federal program through the end of 2005 to help the commercial property and casualty insurance industry cover claims related to future losses resulting from acts of terrorism and requires insurers to offer coverage for acts of terrorism in all commercial property and casualty policies. As a result, we are prohibited from adding certain terrorism exclusions to those policies written by insurers in our group that write business in the U.S. On December 22, 2005, the Terrorism Risk Insurance Extension Act of 2005, or TRIEA, was enacted. TRIEA extended TRIA through December 31, 2007 and made several changes in the program, including the elimination of several previously covered lines. The deductible for each insurer was increased to 17.5% and 20% of direct earned premiums in 2006 and 2007, respectively. For losses in excess of an insurer's deductible, the Insurance Companies will retain an additional 10% and 15% of the excess losses in 2006 and 2007, respectively, with the balance to be covered by the Federal government up to an aggregate cap of insured losses of $25 billion in 2006 and $27.5 billion in 2007. Also, TRIEA established a new program trigger under which Federal compensation will become available only if aggregate insured losses sustained by all insurers exceed $50 million from a certified act of terrorism occurring after March 31, 2006 and $100 million for certified acts occurring on or after January 1, 2007. On December 26, 2007, the Terrorism Risk Insurance Program Reauthorization Act of 2007 ("TRIPRA") was enacted. TRIPRA, among other provisions, extends for seven years the program established under TRIA, as amended. The imposition of these TRIA deductibles could have an adverse effect on our results of operations. Potential future changes to TRIA, including the increases in deductibles and copays and elimination of domestic terrorism coverage proposed by the current administration, could also adversely affect us by causing our reinsurers to increase prices or withdraw from certain markets where terrorism coverage is required. As a result of TRIA, we are required to offer coverage for certain terrorism risks that we may normally exclude. Occasionally in our marine business, such coverage falls outside of our normal reinsurance program. In such cases, our only reinsurance would be the protection afforded by TRIA.
22
Our Lloyd's Operations are subject to regulation in the United States in addition to being regulated in the United Kingdom, as discussed below. The Lloyd's market is licensed to engage in insurance business in Illinois, Kentucky and the U.S. Virgin Islands and operates as an eligible excess and surplus lines insurer in all states and territories except Kentucky and the U.S. Virgin Islands. Lloyd's is also an accredited reinsurer in all states and territories of the United States. Lloyd's maintains various trust funds in the state of New York to protect its United States business and is therefore subject to regulation by the New York Insurance Department, which acts as the domiciliary department for Lloyd's U.S. trust funds. There are deposit trust funds in other states to support Lloyd's reinsurance and excess and surplus lines insurance business.
From time to time, various regulatory and legislative changes have been proposed in the insurance and reinsurance industry. Among the proposals that have in the past been or are at present being considered are the possible introduction of federal regulation in addition to, or in lieu of, the current system of state regulation of insurers and proposals in various state legislatures (some of which have been enacted) to conform portions of their insurance laws and regulations to various model acts adopted by the NAIC. We are unable to predict whether any of these laws and regulations will be adopted, the form in which any such laws and regulations would be adopted, or the effect, if any, these developments would have on our operations and financial condition.
United Kingdom
Our United Kingdom subsidiaries and our Lloyd's Operations are subject to regulation by the FSA, as established by the Financial Services and Markets Act 2000. Our Lloyd's Operations is also subject to supervision by the Council of Lloyd's. The FSA has been granted broad authorization and intervention powers as they relate to the operations of all insurers, including Lloyd's syndicates, operating in the United Kingdom. Lloyd's is authorized by the FSA and is required to implement certain rules prescribed by the FSA, which it does by the powers it has under the Lloyd's Act 1982 relating to the operation of the Lloyd's market. Lloyd's prescribes, in respect of its managing agents and corporate members, certain minimum standards relating to their management and control, solvency and various other requirements. The FSA directly monitors Lloyd's managing agents' compliance with the systems and controls prescribed by Lloyd's. If it appears to the FSA that either Lloyd's is not fulfilling its delegated regulatory responsibilities, or that managing agents are not complying with the applicable regulatory rules and guidance, the FSA may intervene at its discretion.
We participate in the Lloyd's market through our ownership of NUAL, Millennium Underwriting Ltd. and Navigators Corporate Underwriters Ltd. NUAL is the managing agent for Syndicate 1221. We controlled 100% of Syndicate 1221's stamp capacity for the 2009 and 2008 underwriting years through our wholly-owned subsidiary, Navigators Corporate Underwriters Ltd., and through both Millennium Underwriting Ltd., another wholly-owned subsidiary, and Navigators Corporate Underwriters Ltd. in 2007, which are referred to as corporate names in the Lloyd's market. By entering into a membership agreement with Lloyd's, Millennium Underwriting Ltd. and Navigators Corporate Underwriters Ltd. undertake to comply with all Lloyd's bye-laws and regulations as well as the provisions of the Lloyd's Acts and the Financial Services and Markets Act that are applicable to it. The operation of Syndicate 1221, as well as Millennium Underwriting Ltd. and Navigators Corporate Underwriters Ltd. and their respective directors, is subject to the Lloyd's supervisory regime.
Underwriting capacity of a member of Lloyd's must be supported by providing a deposit (referred to as "Funds at Lloyd's") in the form of cash, securities or letters of credit in an amount determined by Lloyd's equal to a specified percentage of the member's underwriting capacity. The amount of such deposit is calculated by each member through the completion of an annual capital adequacy exercise. The results of this exercise are submitted to Lloyd's for approval. Lloyd's then advises the member of the amount of deposit that is required. The consent of the Council of Lloyd's may be required when a managing agent of a syndicate proposes to increase underwriting capacity for the following underwriting year.
23
If the managing agency concludes that an appropriate reinsurance to close for a syndicate that it manages cannot be determined or negotiated on commercially acceptable terms in respect of a particular underwriting year, it must determine that the underwriting year remain open and be placed into run-off. During this period there cannot be a release of the Funds at Lloyd's of a corporate member that is a member of that syndicate without the consent of Lloyd's and such consent will only be considered where the member has surplus funds at Lloyd's.
The Council of Lloyd's has wide discretionary powers to regulate members' underwriting at Lloyd's. It may, for instance, change the basis on which syndicate expenses are allocated or vary the Funds at Lloyd's ratio or the investment criteria applicable to the provision of Funds at Lloyd's. Exercising any of these powers might affect the return on an investment of the corporate member in a given underwriting year. Further, it should be noted that the annual business plans of a syndicate are subject to the review and approval of the Lloyd's Franchise Board. The Lloyd's Franchise Board was formally constituted on January 1, 2003. The Franchise Board is responsible for setting risk management and profitability targets for the Lloyd's market and operates a business planning and monitoring process for all syndicates.
Corporate members continue to have insurance obligations even after all their underwriting years have been closed by reinsurance to close. In order to continue to perform these obligations, corporate members are required to stay in existence; accordingly, there continues to be an administrative and financial burden for corporate members between the time their memberships have ceased and the time their insurance obligations are extinguished, including the completion of financial accounts in accordance with the Companies Act 1985.
If a member of Lloyd's is unable to pay its debts to policyholders, such debts may be payable by the Lloyd's Central Fund, which acts similarly to state guaranty funds in the United States. If Lloyd's determines that the Central Fund needs to be increased, it has the power to assess premium levies on current Lloyd's members. The Council of Lloyd's has discretion to call or assess up to 3% of a member's underwriting capacity in any one year as a Central Fund contribution.
Competition
The property and casualty insurance industry is highly competitive. We face competition from both domestic and foreign insurers, many of whom have longer operating histories and greater financial, marketing and management resources. Competition in the types of insurance in which we are engaged is based on many factors, including our perceived overall financial strength, pricing and other terms and conditions of products and services offered, business experience, marketing and distribution arrangements, agency and broker relationships, levels of customer service (including speed of claims payments), product differentiation and quality, operating efficiencies and underwriting. Furthermore, insureds tend to favor large, financially strong insurers, and we face the risk that we will lose market share to higher rated insurers.
Another competitive factor in the industry is the entrance of other financial services providers such as banks and brokerage firms into the insurance business. These efforts pose new challenges to insurance companies and agents from financial services companies traditionally not involved in the insurance business.
24
Employees
As of December 31, 2009, we had 503 full-time employees of which 408 were located in the United States, 85 in the United Kingdom, 4 in Belgium, 3 in Sweden and 3 in Denmark.
Available Information
This report and all other filings made by the Company with the SEC pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act are made available to the public by the SEC. All filings can be read and copied at the SEC Public Reference Room, located at 100 F Street, NE, Washington, DC 20549. Information pertaining to the operation of the Public Reference Room can be obtained by calling 1-800-SEC-0330. We are an electronic filer, so all reports, proxy and information statements, and other information can be found at the SEC website, www.sec.gov . Our website address is http://www.navg.com . Through our website at http://www.navg.com/finance/sec_filings.phtml, we make available, free of charge, our annual report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and all amendments to those reports as soon as reasonably practicable after such material is electronically filed with or furnished to the SEC. The annual report to stockholders, press releases and recordings of our earnings release conference calls are also provided on our website.
25
Item 1A. RISK FACTORS
You should carefully consider each of the risks and uncertainties described below and elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, as well as any amendments or updates reflected in subsequent filings with the SEC. We believe these risks and uncertainties, individually or in the aggregate, could cause our actual results to differ materially from expected and historical results and could materially and adversely affect our business operations. Further, additional risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we currently deem immaterial may also impair our results and business operations.
The continuing volatility in the financial markets and the current recession could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
The financial market experienced significant volatility worldwide from the third quarter of 2008 through 2009. Although the U.S. and foreign governments have taken various actions to try to stabilize the financial markets, it is unclear whether those actions will be effective. Therefore, the financial market volatility and the resulting negative economic impact could continue and it is possible that it may be prolonged.
Although we continue to monitor market conditions, we cannot predict future market conditions or their impact on our stock price or investment portfolio. Depending on market conditions, we could incur future additional realized and unrealized losses, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition. These economic conditions have had an adverse impact on the availability and cost of credit resources generally, which could negatively affect our ability to obtain letters of credit utilized by our Lloyd's Operations to underwrite business through Lloyd's.
In addition, the continuing financial market volatility and economic downturn could have a material adverse affect on our insureds, agents, claimants, reinsurers, vendors and competitors. Certain of the actions U.S. and foreign governments have taken or may take in response to the financial market crisis have impacted certain property and casualty insurance carriers. The U.S. and foreign governments are actively taking steps to implement additional measures to stabilize the financial markets and stimulate the economy, and it is possible that these measures could further affect the property and casualty insurance industry and its competitive landscape.
Our business is concentrated in marine and energy, specialty liability and professional liability insurance, and if market conditions change adversely, or we experience large losses in these lines, it could have a material adverse effect on our business.
As a result of our strategy to focus on specialty products in niches where we have underwriting and claims handling expertise and to decline business where pricing does not afford what we consider to be acceptable returns, our business is concentrated in the marine and energy, specialty liability and professional liability lines of business. If our results of operations from any of these lines are less favorable for any reason, including lower demand for our products on terms and conditions that we find appropriate, flat or decreased rates for our products or increased competition, the reduction could have a material adverse effect on our business.
26
We are exposed to cyclicality in our business that may cause material fluctuations in our results.
The property/casualty insurance business generally, and the marine insurance business specifically, have historically been characterized by periods of intense price competition due to excess underwriting capacity as well as periods when shortages of underwriting capacity have permitted attractive premium levels. We have reduced business during periods of severe competition and price declines and grown when pricing allowed an acceptable return. We expect that our business will continue to experience the effects of this cyclicality which, over the course of time, could result in material fluctuations in our premium volume, revenues or expenses.
We may not be successful in developing our new specialty lines which could cause us to experience losses.
Since 2001, we have entered into a number of new specialty lines of business, primarily professional liability, excess casualty, primary casualty, inland marine, middle markets and commercial automobile insurance. We continue to look for appropriate opportunities to diversify our business portfolio by offering new lines of insurance in which we believe we have sufficient underwriting and claims expertise. However, because of our limited history in these new lines, there is limited financial information available to help us estimate sufficient reserve amounts for these lines and to help evaluate whether we will be able to successfully develop these new lines or the likely ultimate losses and expenses associated with these new lines. Due to our limited history in these lines, we may have less experience managing their development and growth than some of our competitors. Additionally, there is a risk that the lines of business into which we expand will not perform at the levels we anticipate.
We may be unable to manage effectively our rapid growth in our lines of business, which may adversely affect our results.
To control our growth effectively, we must successfully manage our new and existing lines of business. This process will require substantial management attention and additional financial resources. In addition, our growth is subject to, among other risks, the risk that we may experience difficulties and incur expenses related to hiring and retaining a technically proficient workforce. Accordingly, we may fail to realize the intended benefits of expanding into new specialty lines and we may fail to realize value from such lines relative to the resources that we invest in them. Any difficulties associated with expanding our current and future lines of business could adversely affect our results of operations.
We may incur additional losses if our loss reserves are insufficient.
We maintain loss reserves to cover our estimated ultimate unpaid liability for losses and loss adjustment expenses with respect to reported and unreported claims incurred as of the end of each accounting period. Reserves do not represent an exact calculation of liability, but instead represent estimates, generally utilizing actuarial projection techniques and judgment at a given accounting date. These reserve estimates are expectations of what the ultimate settlement and administration of claims will cost based on our assessment of facts and circumstances then known, review of historical settlement patterns, estimates of trends in claims severity, frequency, legal theories of liability and other factors. Both internal and external events, including changes in claims handling procedures, economic inflation, legal trends and legislative changes, may affect the reserve estimation process. Many of these items are not directly quantifiable, particularly on a prospective basis. Additionally, there may be significant lags between the occurrence of the insured event and the time it is actually reported to the insurer. We continually refine reserve estimates in a regular ongoing process as historical loss experience develops and additional claims are reported and settled. Adjustments to reserves are reflected in the results of the periods in which the estimates are changed. Because establishment of reserves is an inherently uncertain process involving estimates, currently established reserves may not be sufficient. If estimated reserves are insufficient, we will incur additional charges to earnings.
27
Our loss reserves include amounts related to short tail and long tail classes of business. Short tail business means that claims are generally reported quickly upon occurrence of an event, making estimation of loss reserves less complex. For the long tail lines, significant periods of time, ranging up to several years or more, may elapse between the occurrence of the loss, the reporting of the loss and the settlement of the claim. The longer the time span between the incidence of a loss and the settlement of the claim, the more likely the ultimate settlement amount will vary. Our longer tail business includes general liability, including construction defect claims, as well as historical claims for asbestos exposures through our marine and aviation businesses and claims relating to our run-off businesses. Our professional liability business, though long tail with respect to settlement period, is produced on a claims-made basis (which means that the policy in-force at the time the claim is filed, rather than the policy in-force at the time the loss occurred, provides coverage) and is therefore, we believe, less likely to result in a significant time lag between the occurrence of the loss and the reporting of the loss. There can be no assurance, however, that we will not suffer substantial adverse prior period development in our business in the future.
In addition to loss reserves, preparation of our financial statements requires us to make many estimates and judgments.
In addition to loss reserves discussed above, the Consolidated Financial Statements contain estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses and related disclosures. On an ongoing basis we evaluate our estimates based on historical experience and other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances. Any significant change in these estimates could adversely affect our results of operations and/or our financial condition.
We may not have access to adequate reinsurance to protect us against losses.
We purchase reinsurance by transferring part of the risk we have assumed to a reinsurance company in exchange for part of the premium we receive in connection with the risk. The availability and cost of reinsurance are subject to prevailing market conditions, both in terms of price and available capacity, which can affect our business volume and profitability. Our reinsurance programs are generally subject to renewal on an annual basis. If we are unable to renew our expiring facilities or to obtain new reinsurance facilities, either our net exposures would increase, which could increase our costs, or, if we were unwilling to bear an increase in net exposures, we would have to reduce the level of our underwriting commitments, especially catastrophe exposed risks, which would reduce our revenues and possibly net income.
Our reinsurers, including the other participants in the marine pool, may not pay on losses in a timely fashion, or at all, which may increase our costs.
Although reinsurance makes the reinsurer liable to us to the extent the risk is transferred or ceded to the reinsurer, ceded reinsurance arrangements do not eliminate our obligation to pay claims to our policyholders. Accordingly, we bear credit risk with respect to our reinsurers. Specifically, our reinsurers may not pay claims made by us on a timely basis, or they may not pay some or all of these claims. Either of these events would increase our costs and could have a material adverse effect on our business.
28
The operations of the marine insurance pool also expose us to reinsurance credit risk from other participants in the marine insurance pool on business written through the 2005 underwriting year. From 1998 through 2005, all business underwritten by the marine insurance pool was written with Navigators Insurance Company as the primary insurer. Navigators Insurance Company then reinsured its exposure in the marine insurance pool to the other participants based on their percentage of participation. From 1983 until 1998, Navigators Insurance Company was the primary insurer for some of the pool business in excess of its participation amount. As a result of these arrangements, we remain primarily liable for claims arising out of those policies written by Navigators Insurance Company on behalf of the marine insurance pool even if one or more of the other participants do not pay the claims they reinsured, which could have a material adverse effect on our business. The marine insurance pool was eliminated beginning with the 2006 underwriting year.
Intense competition for our products could harm our ability to maintain or increase our profitability and premium volume.
The property and casualty insurance industry is highly competitive. We face competition from both domestic and foreign insurers, many of whom have longer operating histories and greater financial, marketing and management resources. Competition in the types of insurance in which we are engaged is based on many factors, including our perceived overall financial strength, pricing and other terms and conditions of products and services offered, business experience, marketing and distribution arrangements, agency and broker relationships, levels of customer service (including speed of claims payments), product differentiation and quality, operating efficiencies and underwriting. Furthermore, insureds tend to favor large, financially strong insurers, and we face the risk that we will lose market share to higher rated insurers.
We may have difficulty in continuing to compete successfully on any of these bases in the future. If competition limits our ability to write new business at adequate rates, our ability to transact business would be materially and adversely affected and our results of operations would be adversely affected.
We may be unable to attract and retain qualified employees.
We depend on our ability to attract and retain qualified executive officers, experienced underwriters and claims professionals and other skilled employees who are knowledgeable about our specialty lines of business. If the quality of our executive officers, underwriting or claims team and other personnel decreases, we may be unable to maintain our current competitive position in the specialty markets in which we operate and be unable to expand our operations into new specialty markets.
Increases in interest rates may cause us to experience losses.
Because of the unpredictable nature of losses that may arise under insurance policies, we may require substantial liquidity at any time. Our investment portfolio, which consists largely of fixed-income investments, is our principal source of liquidity. The market value of our fixed-income investments is subject to fluctuation depending on changes in prevailing interest rates and various other factors. We do not hedge our investment portfolio against interest rate risk. Increases in interest rates during periods when we must sell fixed-income securities to satisfy liquidity needs may result in realized investment losses.
Our investment portfolio is subject to certain risks that could adversely affect our results of operations and/or financial condition.
Although our investment policy guidelines emphasize total investment return in the context of preserving and enhancing shareholder value and statutory surplus of the insurance subsidiaries, our investments are subject to market-wide risks and fluctuations, as well as to risks inherent in particular types of securities. Due to these risks we may not be able to realize our investment objectives. In addition, we may be forced to liquidate investments at times and prices that are not optimal, which could have an adverse affect on our results of operations. Investment losses could significantly decrease our asset base, thereby adversely affecting our ability to conduct business and pay claims.
29
We are exposed to significant capital market risks related to changes in interest rates, credit spreads, equity prices and foreign exchange rates which may adversely affect our results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
We are exposed to significant capital markets risk related to changes in interest rates, credit spreads, equity prices and foreign currency exchange rates. If significant, declines in equity prices, changes in interest rates, changes in credit spreads and the strengthening or weakening of foreign currencies against the U.S. dollar, individually or in tandem, could have a material adverse effect on our consolidated results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
Our exposure to interest rate risk relates primarily to the market price and cash flow variability associated with changes in interest rates. Our investment portfolio contains interest rate sensitive instruments, such as fixed income securities, which may be adversely affected by changes in interest rates from governmental monetary policies, domestic and international economic and political conditions and other factors beyond our control. A rise in interest rates would reduce the fair value of our investment portfolio. It would also provide the opportunity to earn higher rates of return on funds reinvested. Conversely, a decline in interest rates would increase the fair value of our investment portfolio. We would then presumably earn lower rates of return on assets reinvested. We may be forced to liquidate investments prior to maturity at a loss in order to cover liabilities. Although we take measures to manage the economic risks of investing in a changing interest rate environment, we may not be able to mitigate the interest rate risk of our assets relative to our liabilities.
Included in our fixed income securities are asset-backed and mortgage-backed securities. Changes in interest rates can expose us to prepayment risks on these investments. In periods of declining interest rates, mortgage prepayments generally increase and mortgage-backed securities are prepaid more quickly, requiring us to reinvest the proceeds at the then current rates.
Our fixed income portfolio is invested in high quality, investment-grade securities. However, we are permitted to invest up to 5% of our book value in below investment-grade high yield fixed income securities. These securities, which pay a higher rate of interest, also have a higher degree of credit or default risk. These securities may also be less liquid in times of economic weakness or market disruptions. While we have put in place procedures to monitor the credit risk and liquidity of our invested assets, it is possible that, in periods of economic weakness, we may experience default losses in our portfolio. This may result in a reduction of net income, capital and cash flows.
We invest a portion of our portfolio in common stock or preferred stocks. The value of these assets fluctuates with the equity markets. In times of economic weakness, the market value and liquidity of these assets may decline, and may impact net income, capital and cash flows.
The functional currencies of the Company's principal insurance and reinsurance subsidiaries are the U.S. dollar, U.K. pound and the Canadian dollar. Exchange rate fluctuations relative to the functional currencies may materially impact our financial position. Certain of our subsidiaries maintain both assets and liabilities in currencies different than their functional currency, which exposes us to changes in currency exchange rates. In addition, locally-required capital levels are invested in local currencies in order to satisfy regulatory requirements and to support local insurance operations regardless of currency fluctuations.
30
Despite our mitigation efforts, an increase in interest rates could have a material adverse effect on our book value.
Capital may not be available in the future, or available on unfavorable terms.
The capital needs of our business are dependent on several factors, including our ability to write new business successfully and to establish premium rates and reserves at levels sufficient to cover our losses. If our current capital becomes insufficient for our future plans, we may need to raise additional capital through the issuance of stock or debt. Otherwise, in the case of insufficient capital, we may need to limit our growth. The terms of an equity or debt offering could be unfavorable, for example, causing dilution to our current shareholders or such securities may have rights, preferences and privileges that are senior to our existing securities. If we were in a situation of having inadequate capital and if we were not able to obtain additional capital, our business, results of operations and financial condition could be adversely affected.
A downgrade in our ratings could adversely impact the competitive positions of our operating businesses.
Ratings are a critical factor in establishing the competitive position of insurance companies. The Insurance Companies are rated by A.M. Best and S&P. A.M. Best's and S&P's ratings reflect their opinions of an insurance company's financial strength, operating performance, strategic position and ability to meet its obligations to policyholders, and are not evaluations directed to investors. Our ratings are subject to periodic review by A.M. Best and S&P. Because these ratings have become an increasingly important factor in establishing the competitive position of insurance companies, if these ratings are reduced, our competitive position in the industry, and therefore our business, could be adversely affected. A significant downgrade could result in a substantial loss of business as policyholders might move to other companies with higher ratings. There can be no assurance that our current ratings will continue for any given period of time. For a further discussion of our ratings, see "Business - Ratings" included herein.
Continued or increased premium levies by Lloyd's for the Lloyd's Central Fund and cash calls for trust fund deposits or a significant downgrade of Lloyd's A.M. Best rating could materially and adversely affect us.
The Lloyd's Central Fund protects Lloyd's policyholders against the failure of a member of Lloyd's to meet its obligations. The Central Fund is a mechanism which in effect mutualizes unpaid liabilities among all members, whether individual or corporate. The fund is available to back Lloyd's policies issued after 1992. Lloyd's requires members to contribute to the Central Fund, normally in the form of an annual contribution, although a special contribution may be levied. The Council of Lloyd's has discretion to call up to 3% of underwriting capacity in any one year.
Policies issued before 1993 have been reinsured by Equitas, an independent insurance company authorized by the Financial Services Authority. However, if Equitas were to fail or otherwise be unable to meet all of its obligations, Lloyd's may take the view that it is appropriate to apply the Central Fund to discharge those liabilities Equitas failed to meet. In that case, the Council of Lloyd's may resolve to impose a special or additional levy on the existing members, including Lloyd's corporate members, to satisfy those liabilities.
Additionally, Lloyd's insurance and reinsurance business is subject to local regulation, and regulators in the United States require Lloyd's to maintain certain minimum deposits in trust funds as protection for policyholders in the United States. These deposits may be used to cover liabilities in the event of a major claim arising in the United States and Lloyd's may require us to satisfy cash calls to meet claims payment obligations and maintain minimum trust fund amounts.
31
Any premium levy or cash call would increase the expenses of Millennium Underwriting Ltd. and Navigators Corporate Underwriters Ltd., our corporate members, without providing compensating revenues, and could have a material adverse effect on our results.
We believe that in the event that Lloyd's rating is downgraded, the downgrade could have a material adverse effect on our ability to underwrite business through our Lloyd's Operations and therefore on our financial condition or results of operations.
Our businesses are heavily regulated, and changes in regulation may reduce our profitability and limit our growth.
Our insurance subsidiaries are subject to extensive regulation and supervision in the jurisdictions in which they conduct business. This regulation is generally designed to protect the interests of policyholders, as opposed to insurers and their stockholders and other investors, and relates to authorization for lines of business, capital and surplus requirements, investment limitations, underwriting limitations, transactions with affiliates, dividend limitations, changes in control, premium rates and a variety of other financial and non-financial components of an insurance company's business.
Virtually all states require insurers licensed to do business in that state to bear a portion of the loss suffered by some insureds as the result of impaired or insolvent insurance companies. The effect of these arrangements could reduce our profitability in any given period or limit our ability to grow our business.
In recent years, the state insurance regulatory framework has come under increased federal scrutiny, and some state legislatures have considered or enacted laws that may alter or increase state authority to regulate insurance companies and insurance holding companies. Further, the NAIC and state insurance regulators are re-examining existing laws and regulations, specifically focusing on modifications to holding company regulations, interpretations of existing laws and the development of new laws. Any proposed or future legislation or NAIC initiatives may be more restrictive than current regulatory requirements or may result in higher costs.
In response to the September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks, the United States Congress has enacted legislation designed to ensure, among other things, the availability of insurance coverage for terrorist acts, including the requirement that insurers provide such coverage in certain circumstances. See "Business - Regulation - United States" included herein for a discussion of the TRIA, TRIEA and TRIPRA legislation.
32
The inability of our subsidiaries to pay dividends to us in sufficient amounts would harm our ability to meet our obligations.
The Parent Company is a holding company and relies primarily on dividends from our subsidiaries to meet our obligations for payment of interest and principal on outstanding debt obligations and corporate expenses. The ability of our insurance subsidiaries to pay dividends to the Parent Company in the future will depend on their statutory surplus, on earnings and on regulatory restrictions. For a discussion of our insurance subsidiaries' current dividend-paying ability, please see "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations-Liquidity and Capital Resources", included herein. The Parent Company and our underwriting subsidiaries are subject to regulation by some states as an insurance holding company. Such regulation generally provides that transactions between companies within our consolidated group must be fair and equitable. Transfers of assets among affiliated companies, certain dividend payments from underwriting subsidiaries and certain material transactions between companies within our consolidated group may be subject to prior notice to, or prior approval by, state regulatory authorities. Our underwriting subsidiaries are also subject to licensing and supervision by government regulatory agencies in the jurisdictions in which they do business. These regulations may set standards of solvency that must be met and maintained, such as the nature of and limitations on investments, the nature of and limitations on dividends to policyholders and stockholders and the nature and extent of required participation in insurance guaranty funds. These regulations may affect our subsidiaries' ability to provide us with dividends.
Catastrophe losses could materially reduce our profitability.
We are exposed to claims arising out of catastrophes, particularly in our marine insurance line of business and our NavTech business. We have experienced, and will experience in the future, catastrophe losses which may materially reduce our profitability or harm our financial condition. Catastrophes can be caused by various natural events, including hurricanes, windstorms, earthquakes, hail, severe winter weather and fires. Catastrophes can also be man-made, such as the World Trade Center attack. The incidence and severity of catastrophes are inherently unpredictable. Although we will attempt to manage our exposure to such events, the frequency and severity of catastrophic events could exceed our estimates, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition.
The market price of Navigators common stock may be volatile.
There has been significant volatility in the market for equity securities. The price of Navigators common stock may not remain at or exceed current levels. In addition to the other risk factors detailed herein, the following factors may have an adverse impact on the market price of Navigators common stock:
| • | actual or anticipated variations in our quarterly results of operations, including the result of catastrophes, |
| • | changes in market valuations of companies in the insurance and reinsurance industry, |
| • | changes in expectations of future financial performance or changes in estimates of securities analysts, |
| • | issuances of common shares or other securities in the future, |
| • | the addition or departure of key personnel, and |
| • | announcements by us or our competitors of acquisitions, investments or strategic alliances. |
Stock markets in the United States often experience price and volume fluctuations. Market fluctuations, as well as general political and economic conditions such as recession or interest rate or currency rate fluctuations, could adversely affect the market price of Navigators common stock.
Item 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
33
Item 2. PROPERTIES
Our executive and administrative office is located at 6 International Drive in Rye Brook, NY. Our lease for this space expires in February 2014. Our underwriting operations are in various locations with non-cancelable operating leases including Charlotte, NC, Chicago, IL, Coral Gables, FL, Corona, CA, Houston, TX, Irvine, CA, New York City, NY, Philadelphia, PA, Pittsburgh, PA, San Francisco, CA, Schaumburg, IL, Seattle, WA, London, England, Antwerp, Belgium, Stockholm, Sweden and Copenhagen, Denmark.
Item 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
We are working with various state insurance regulators on a matter involving administrative fees charged by a program administrator on certain personal umbrella insurance policies underwritten by Navigators Insurance Company that were outside of Navigators Insurance Company's filed rates and forms. Following discovery of the issue, Navigators Insurance Company approached regulators in the affected states to resolve these matters, and is currently making refunds to policyholders for policy fees collected from the time of discovery of the issue that did not comply with Navigators' filed rates. In addition, Navigators Insurance Company has terminated its relationship with the program administrator effective August 1, 2009 and has ensured that fees will not be collected on any policies going forward unless such fees are permitted by each state in which they are charged. Other operating expenses for the second quarter 2009 include a $1.3 million charge related to this matter. Navigators Insurance Company may be subject to additional fines, refund obligations and other exposure with respect to the past fees charged. We cannot at this time reasonably estimate the additional cost of resolving this matter. However, we do not expect that it will have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
Our subsidiaries are subject to disputes, including litigation and arbitration, arising in the ordinary course of their insurance businesses, including claims asserting extra contractual obligations in connection with the underwriting of policies and handling of claims. Our estimates of the costs of settling such matters are reflected in its aggregate reserves for losses and loss expenses, and we do not believe that the ultimate outcome of such matters will have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
Item 4. SUBMISSION OF MATTERS TO A VOTE OF SECURITY HOLDERS
There were no matters submitted to a vote of security holders during the fourth quarter of 2009.
34
Part II
Item 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT'S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Market Information
The Company's common stock is traded over-the-counter on NASDAQ under the symbol NAVG. Over-the-counter market quotations reflect inter-dealer prices, without retail mark-up, mark-down or commissions and may not necessarily represent actual transactions.
The high, low and closing trade prices for the four quarters of 2009 and 2008 were as follows:
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| High | Low | Close | High | Low | Close | |||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
First Quarter | $ | 57.58 | $ | 45.30 | $ | 47.18 | $ | 65.01 | $ | 50.91 | $ | 54.40 | ||||||||||||
Second Quarter | $ | 49.75 | $ | 42.80 | $ | 44.43 | $ | 56.99 | $ | 47.23 | $ | 54.05 | ||||||||||||
Third Quarter | $ | 56.29 | $ | 43.59 | $ | 55.00 | $ | 66.74 | $ | 43.46 | $ | 58.00 | ||||||||||||
Fourth Quarter | $ | 57.64 | $ | 45.83 | $ | 47.11 | $ | 60.50 | $ | 39.29 | $ | 54.91 | ||||||||||||
Information provided to us by our transfer agent and proxy solicitor indicates that there are approximately 321 holders of record and 4,142 beneficial holders of our common stock.
35
Five Year Stock Performance Graph
The Five Year Stock Performance Graph and related Cumulative Indexed Returns table, as presented below, which were prepared with the aid of S&P, reflects the cumulative return on the Company's common stock, the S&P 500 Index and the Insurance Index assuming an original investment in each of $100 on December 31, 2004 (the "Base Period") and reinvestment of dividends to the extent declared. Cumulative returns for each year subsequent to 2004 are measured as a change from this Base Period.
The comparison of five year cumulative returns among the Company, the companies listed in the Standard & Poor's 500 Index ("S&P 500 Index") and the S&P Property & Casualty Insurance Index (the "Insurance Index") is as follows:
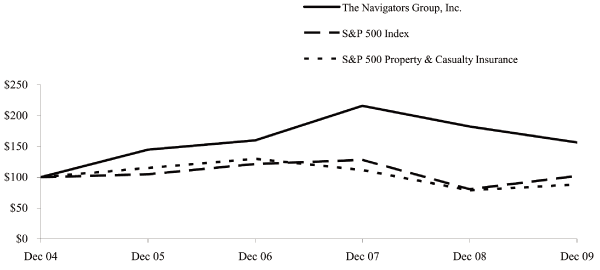
| Base | Cumulative Indexed Returns | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | Years Ending December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Company / Index | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Navigators Group, Inc. | 100 | 144.84 | 160.01 | 215.88 | 182.36 | 156.45 | ||||||||||||||||||
S&P 500 Index | 100 | 104.91 | 121.48 | 128.16 | 80.74 | 102.11 | ||||||||||||||||||
S&P 500 Property & Casualty Insurance | 100 | 115.11 | 129.93 | 111.79 | 78.91 | 88.55 | ||||||||||||||||||
36
The following Annual Return Percentage table reflects the annual return on the Company's common stock, the S&P 500 Index and the Insurance Index including reinvestment of dividends to the extent declared.
| Annual Return Percentage | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Years Ending December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Company / Index | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | |||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
The Navigators Group, Inc. | 44.84 | 10.48 | 34.91 | -15.52 | -14.21 | |||||||||||||||
S&P 500 Index | 4.91 | 15.79 | 5.49 | -37.00 | 26.46 | |||||||||||||||
S&P 500 Property & Casualty Insurance | 15.11 | 12.87 | -13.96 | -29.41 | 12.21 | |||||||||||||||
Dividends
We have not paid or declared any cash dividends on our common stock. While there presently is no intention to pay cash dividends on the common stock, future declarations, if any, are at the discretion of our Board of Directors and the amounts of such dividends will be dependent upon, among other factors, our results of operations and cash flow, financial condition and business needs, restrictive covenants under our credit facility, the capital and surplus requirements of our subsidiaries and applicable government regulations.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
None
Use of Proceeds from Public Offering of Debt Securities
None
Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer
In November 2009, the Company's Board of Directors adopted a stock repurchase program for up to $35 million of our common stock through December 31, 2010. Purchases are permitted from time to time at prevailing prices in open market or privately negotiated transactions. The timing and amount of purchases under the program depend on a variety of factors, including the trading price of the stock, market conditions and corporate and regulatory considerations. Through December 31, 2009, we purchased 141,576 shares of our common stock at an aggregate cost of $6.8 million. From January 1, 2010 through February 22, 2010, the Parent Company purchased an additional 300,000 shares of its common stock in the open market at an aggregate cost of $13.0 million.
In October 2007, the Company's Board of Directors adopted a stock repurchase program for up to $30 million of the Company's common stock. Purchases were made from time to time at prevailing prices in open market or privately negotiated transactions through the expiration of the program on December 31, 2008. The timing and amount of purchases under the program were dependent on a variety of factors, including the trading price of the stock, market conditions and corporate and regulatory considerations. In total, we purchased 224,754 shares of our common stock at an aggregate cost of $11.5 million.
37
The following table summarizes the Parent Company's purchases of its common stock during 2008 and 2009:
| Number of | ||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Dollar Value | |||||||||||||||
| Total | Purchased | of Shares that | ||||||||||||||
| Number | Average | Under Publicly | May Yet Be | |||||||||||||
| of Shares | Cost Paid | Announced | Purchased Under | |||||||||||||
| Purchased | Per Share | Program | the Program (1) | |||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands, except per share) | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
January 2008 | - | - | - | $ | 30,000 | |||||||||||
February 2008 | 30,202 | $ | 54.66 | 30,202 | $ | 28,349 | ||||||||||
March 2008 | 105,824 | $ | 53.58 | 105,824 | $ | 22,679 | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Subtotal first quarter | 136,026 | $ | 53.82 | 136,026 | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
April 2008 | 50,000 | $ | 49.90 | 50,000 | $ | 20,184 | ||||||||||
May 2008 | - | - | - | $ | 20,184 | |||||||||||
June 2008 | - | - | - | $ | 20,184 | |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Subtotal second quarter | 50,000 | $ | 49.90 | 50,000 | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
July 2008 | 38,728 | $ | 44.51 | 38,728 | $ | 18,460 | ||||||||||
August 2008 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
September 2008 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Subtotal third quarter | 38,728 | $ | 44.51 | 38,728 | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Total December 31, 2008 | 224,754 | $ | 51.34 | 224,754 | $ | - | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Balance as of the end of the month indicated. The stock repurchase program adopted in October 2007 for up to $30 million expired on December 31, 2008. |
| Number of | ||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Dollar Value | |||||||||||||||
| Total | Purchased | of Shares that | ||||||||||||||
| Number | Average | Under Publicly | May Yet Be | |||||||||||||
| of Shares | Cost Paid | Announced | Purchased Under | |||||||||||||
| Purchased | Per Share | Program | the Program (1) | |||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands, except per share) | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
October 2009 | - | - | - | $ | 35,000 | |||||||||||
November 2009 | 29,021 | $ | 47.30 | 29,021 | $ | 33,627 | ||||||||||
December 2009 | 112,555 | $ | 47.83 | 112,555 | $ | 28,243 | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Subtotal fourth quarter | 141,576 | $ | 47.72 | 141,576 | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Total December 31, 2009 | 141,576 | $ | 47.72 | 141,576 | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Balance as of the end of the month indicated. |
38
Item 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
The following table sets forth selected consolidated financial data including consolidated financial information of the Company for each of the last five calendar years, derived from the Company's audited Consolidated Financial Statements. You should read the table in conjunction with Item 7, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations", and Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data", included herein.
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | ||||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Operating Information: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Gross written premiums | $ | 1,044,918 | $ | 1,084,922 | $ | 1,070,707 | $ | 970,790 | $ | 779,579 | ||||||||||
Net written premiums | 701,255 | 661,615 | 645,796 | 520,807 | 380,659 | |||||||||||||||
Net earned premiums | 683,363 | 643,976 | 601,977 | 468,323 | 338,551 | |||||||||||||||
Net investment income | 75,512 | 76,554 | 70,662 | 56,895 | 37,069 | |||||||||||||||
Net realized gains (losses) (1) | (2,660 | ) | (38,299 | ) | 2,006 | (1,026 | ) | 1,238 | ||||||||||||
Total revenues | 762,880 | 683,666 | 676,659 | 526,594 | 385,219 | |||||||||||||||
Income before income taxes | 86,848 | 68,731 | 139,182 | 106,617 | 33,754 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | 63,158 | 51,692 | 95,620 | 72,563 | 23,564 | |||||||||||||||
Net income per share: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 3.73 | $ | 3.08 | $ | 5.69 | $ | 4.34 | $ | 1.74 | ||||||||||
Diluted | $ | 3.65 | $ | 3.04 | $ | 5.62 | $ | 4.30 | $ | 1.73 | ||||||||||
Average common shares outstanding (000s): | ||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | 16,935 | 16,802 | 16,812 | 16,722 | 13,528 | |||||||||||||||
Diluted | 17,322 | 16,992 | 17,005 | 16,856 | 13,657 | |||||||||||||||
Combined loss & expense ratio (2) : | ||||||||||||||||||||
Loss ratio | 63.8 | % | 61.0 | % | 56.6 | % | 57.7 | % | 69.6 | % | ||||||||||
Expense ratio | 33.4 | % | 32.8 | % | 30.9 | % | 30.1 | % | 31.7 | % | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Total | 97.2 | % | 93.8 | % | 87.5 | % | 87.8 | % | 101.3 | % | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Balance sheet information (at end of year): | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total investments and cash | $ | 2,056,587 | $ | 1,917,715 | $ | 1,767,301 | $ | 1,475,910 | $ | 1,182,236 | ||||||||||
Total assets | 3,453,994 | 3,349,580 | 3,143,771 | 2,956,686 | 2,583,249 | |||||||||||||||
Gross losses and LAE reserves | 1,920,286 | 1,853,664 | 1,648,764 | 1,607,555 | 1,557,991 | |||||||||||||||
Net losses and LAE reserves | 1,112,934 | 999,871 | 847,303 | 696,116 | 578,976 | |||||||||||||||
Senior notes | 114,010 | 123,794 | 123,673 | 123,560 | - | |||||||||||||||
Stockholders' equity | 801,519 | 689,317 | 662,106 | 551,343 | 470,238 | |||||||||||||||
Common shares outstanding (000s) | 16,846 | 16,856 | 16,873 | 16,736 | 16,617 | |||||||||||||||
Book value per share (3) | $ | 47.58 | $ | 40.89 | $ | 39.24 | $ | 32.94 | $ | 28.30 | ||||||||||
Statutory surplus of Navigators Insurance Company | $ | 645,820 | $ | 581,166 | $ | 578,668 | $ | 524,188 | $ | 356,484 | ||||||||||
| (1) | Includes Net other-than-temporary impairment losses recognized in earnings. | |
| (2) | Calculated based on earned premiums. | |
| (3) | Calculated as stockholders' equity divided by actual shares outstanding as of the date indicated. |
39
Item 7. MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with our Consolidated Financial Statements and accompanying notes which appear elsewhere in this Form 10-K . It contains forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. Please see "Note on Forward-Looking Statements" and "Risk Factors" for more information. Our actual results could differ materially from those anticipated in these forward-looking statements as a result of various factors, including those discussed below and elsewhere in this Form 10-K .
Overview
We are an international insurance company focusing on specialty products within the overall property/casualty insurance market. Our largest product line and most long-standing area of specialization is ocean marine insurance. We have also developed specialty niches in professional liability insurance and in specialty liability insurance primarily consisting of contractors' liability and primary and excess casualty coverages.
Our revenue is primarily comprised of premiums and investment income. We derive our premiums primarily from business written by wholly-owned underwriting management companies which produce, manage and underwrite insurance and reinsurance for us. Our products are distributed through multiple channels, utilizing global, national and regional retail and wholesale insurance brokers.
We conduct operations through our Insurance Companies and our Lloyd's Operations segments. The Insurance Companies segment consists of Navigators Insurance Company, which includes a United Kingdom Branch (the "U.K. Branch"), and Navigators Specialty Insurance Company, which underwrites specialty and professional liability insurance on an excess and surplus lines basis. All of the insurance business written by Navigators Specialty Insurance Company is fully reinsured by Navigators Insurance Company pursuant to a 100% quota share reinsurance agreement. Our Lloyd's Operations segment includes Navigators Underwriting Agency Ltd. ("NUAL"), a Lloyd's of London ("Lloyd's") underwriting agency which manages Lloyd's Syndicate 1221 ("Syndicate 1221"). Our Lloyd's Operations primarily underwrite marine and related lines of business along with offshore energy, professional liability insurance and construction coverages for onshore energy business at Lloyd's through Syndicate 1221. We controlled 100% of Syndicate 1221's stamp capacity for the 2009 and 2008 underwriting years through our wholly-owned subsidiary, Navigators Corporate Underwriters Ltd., and through both Millennium Underwriting Ltd., another wholly-owned subsidiary, and Navigators Corporate Underwriters Ltd. in 2007, which are referred to as corporate names in the Lloyd's market. We have also established underwriting agencies in Antwerp, Belgium, Stockholm, Sweden and Copenhagen, Denmark, which underwrite risks pursuant to binding authorities with NUAL into Syndicate 1221.
Effective in 2009, we reclassified certain business lines within our segments, which had no effect on the segment classifications of the Insurance Companies and Lloyd's Operations. Underwriting data for prior periods has been reclassified to reflect these changes.
| • | The offshore energy business, formerly included in the "Marine and Energy" businesses of the Insurance Companies and Lloyd's Operations, is now included in the Insurance Companies' and Lloyd's Operations' "Property Casualty" businesses. |
| • | The marine lines within both the Insurance Companies and Lloyd's Operations are now presented as "Marine" instead of "Marine and Energy", since the offshore energy business has now been reclassified to "Property Casualty". |
| • | Engineering and construction, European Property and other run-off business, formerly included in the "Other" category of business within the Insurance Companies and Lloyd's Operations, are now included under "Property Casualty". |
| • | The "Middle Markets" business, formerly broken out separately in the Insurance Companies, is now included in the Insurance Companies' "Property Casualty" business. |
40
While management takes into consideration a wide range of factors in planning our business strategy and evaluating results of operations, there are certain factors that management believes are fundamental to understanding how we are managed. First, underwriting profit is consistently emphasized as a primary goal, above premium growth. Management's assessment of our trends and potential growth in underwriting profit is the dominant factor in its decisions with respect to whether or not to expand a business line, enter into a new niche, product or territory or, conversely, to contract capacity in any business line. In addition, management focuses on controlling the costs of our operations. Management believes that careful monitoring of the costs of existing operations and assessment of costs of potential growth opportunities are important to our profitability. Access to capital also has a significant impact on management's outlook for our operations. The Insurance Companies' operations and ability to grow their business and take advantage of market opportunities are constrained by regulatory capital requirements and rating agency assessments of capital adequacy.
Management's decisions are also greatly influenced by access to specialized underwriting and claims expertise in our lines of business. We have chosen to operate in specialty niches with certain common characteristics which we believe provide us with the opportunity to use our technical underwriting expertise in order to realize underwriting profit. As a result, we have focused on underserved markets for businesses characterized by higher severity and low frequency of loss where we believe our intellectual capital and financial strength bring meaningful value. In contrast, we have avoided niches that we believe have a high frequency of loss activity and/or are subject to a high level of regulatory requirements, such as workers compensation and personal automobile insurance, because we do not believe our technical expertise is of as much value in these types of businesses. Examples of niches that have the characteristics we look for include bluewater hull which provides coverage for physical damage to, for example, highly valued cruise ships, and directors and officers liability ("D&O") insurance which covers litigation exposure of a corporation's directors and officers. These types of exposures require substantial technical expertise. We attempt to mitigate the financial impact of severe claims on our results by conservative and detailed underwriting, prudent use of reinsurance and a balanced portfolio of risks.
Our total gross written premiums declined 4% in 2009 primarily due to several factors:
| • | Our construction liability lines decreased 39% due to both a decline in demand resulting from current economic conditions as well as increased competition due to new entrants into the market. |
| • | A 24% decline in our offshore energy lines primarily resulting from a planned reduction in our Gulf of Mexico exposure as market pricing and terms did not meet our underwriting standards. |
Partially offsetting these factors were:
| • | A 39% increase in our D&O insurance lines due to continued expansion of this business. |
| • | Improved pricing conditions across the majority of our lines of business, resulting in an overall 4% increase in average renewal rates. Pricing conditions have stabilized after experiencing declines across all of our lines in 2008 and were driven by a flight to quality after the market turmoil at the end of 2008. |
In 2009, we decreased our use of quota share reinsurance and expanded our use of excess-of-loss reinsurance. This change in the mix of our reinsurance resulted in an increase in our retention in 2009, which translated into higher net written premiums and net earned premiums in 2009 compared to 2008.
Our net investment income declined 1% in 2009. Our pre-tax average investment yield declined to 3.8% from 4.1% in 2008 resulting from lower short-term yields. Our total investment portfolio continued to increase in 2009 and had exceeded $2 billion at the end of 2009. We experienced significantly lower investment impairments in our portfolio in 2009 as the financial markets experienced a period of stability compared to the second half of 2008.
41
Our overall loss ratio of 63.8% for 2009 increased compared to 2008 due primarily to a $42 million decline in net prior year savings. Although we continued to realize prior year savings in our contractors liability lines, we experienced unfavorable prior year development in our D&O and lawyers lines relating to unfavorable development in the 2006 and 2005 through 2008 underwriting years, respectively. Additional unfavorable prior year development in our Insurance Company marine liability lines resulted in a 2009 underwriting loss in both the Marine and Professional Liability divisions within the Insurance Companies segment.
The discussions that follow include tables that contain both our consolidated and segment operating results for the last three calendar years. In presenting our financial results, we have discussed our performance with reference to underwriting profit or loss and the related combined ratio, both of which are non-GAAP measures of underwriting profitability. We consider such measures, which may be defined differently by other companies, to be important in the understanding of our overall results of operations. Underwriting profit or loss is calculated from net earned premium, less the sum of net losses and LAE, commission expense, other operating expenses and commission income and other income (expense). The combined ratio is derived by dividing the sum of net losses and LAE, commission expense, other operating expenses and commission income and other income (expense) by net earned premium. A combined ratio of less than 100% indicates an underwriting profit and over 100% indicates an underwriting loss.
For additional information regarding our business, see "Business-Overview", included herein.
Critical Accounting Policies
It is important to understand our accounting policies in order to understand our financial statements. Management considers certain of these policies to be critical to the presentation of the financial results, since they require management to make estimates and assumptions. These estimates and assumptions affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues, expenses, and related disclosures at the financial reporting date and throughout the reporting period. Certain of the estimates result from judgments that can be subjective and complex and, consequently, actual results may differ from these estimates, which would be reflected in future periods.
Our most critical accounting policies involve the reporting of the reserves for losses and LAE (including losses that have occurred but were not reported to us by the financial reporting date), reinsurance recoverables, written and unearned premium, the recoverability of deferred tax assets, the impairment of investment securities and accounting for Lloyd's results.
Reserves for Losses and Loss Adjustment Expenses
Reserves for losses and loss adjustment expenses represent an estimate of the expected cost of the ultimate settlement and administration of losses, based on facts and circumstances then known. Actuarial methodologies are employed to assist in establishing such estimates and include judgments relative to estimates of future claims severity and frequency, length of time to develop to ultimate, judicial theories of liability and other third party factors which are often beyond our control. No assurance can be given that actual claims made and related payments will not be in excess of the amounts reserved. During the loss settlement period, it often becomes necessary to refine and adjust the estimates of liability on a claim either upward or downward. Even after such adjustments, ultimate liability may exceed or be less than the revised estimates.
The numerous factors that contribute to the inherent uncertainty in the process of establishing loss reserves include: interpreting loss development activity, emerging economic and social trends, inflation, changes in the regulatory and judicial environment and changes in our operations, including changes in underwriting standards and claims handling procedures. The process of establishing loss reserves is complex and imprecise as it must take into account many variables that are subject to the outcome of future events. As a result, informed subjective judgments as to our ultimate exposure to losses are an integral component of our loss reserving process.
42
Our actuaries generally calculate the IBNR loss reserves for each line of business by underwriting year for major products principally using two standard actuarial methodologies which are projection or extrapolation techniques: the loss ratio method and the Bornheutter-Ferguson method. The loss ratio method is used to calculate the IBNR for the two most current underwriting years while the Bornheutter-Ferguson method is used to calculate the IBNR for all prior underwriting years, except as otherwise described below. Such methodologies are supplemented in most instances by the loss development method and the frequency/severity method which are used to analyze and better comprehend loss development patterns and trends in the data when making selections and judgments under the loss ratio method and the Bornheutter-Ferguson method. In utilizing these methodologies, each of which is generally applicable to both long tail and short tail lines of business and all of which are described below, to develop our IBNR loss reserves, a key objective of our actuaries is to identify aberrations and systemic changes occurring within historical experience and accurately adjust for them so that the future can be projected more reliably. This process requires the substantial use of informed judgment and is inherently uncertain.
There are instances in which facts and circumstances require a deviation from the general process described above. Three such instances relate to the IBNR loss reserve processes for our 2008 Hurricanes losses, our 2005 Hurricanes losses and our asbestos exposures, where extrapolation techniques are not applied, except in a limited way, given the unique nature of hurricane losses and limited population of marine excess policies with potential asbestos exposures. In such circumstances, inventories of the policy limits exposed to losses coupled with reported losses are analyzed and evaluated principally by claims personnel and underwriters to establish IBNR loss reserves.
A brief summary of each actuarial method discussed above follows:
Loss ratio method : This method is based on the assumption that ultimate losses vary proportionately with premiums. Pursuant to the loss ratio method, IBNR loss reserves are calculated by multiplying the earned premium by an expected ultimate loss ratio to estimate the ultimate losses for each underwriting year, then subtracting the reported losses, consisting of paid losses and case loss reserves, to determine the IBNR loss reserve amount. The ultimate loss ratios applied are the Company's best estimates for each underwriting year and are generally determined after evaluating a number of factors which include: information derived by underwriters and actuaries in the initial pricing of the business, the ultimate loss ratios established in the prior accounting period and the related judgments applied, the ultimate loss ratios of previous underwriting years, premium rate changes, underwriting and coverage changes, changes in terms and conditions, legislative changes, exposure trends, loss development trends, claim frequency and severity trends, paid claims activity, remaining open case reserves and industry data where deemed appropriate. Such factors are also evaluated when selecting ultimate loss ratios and/or loss development factors in the methods described below.
Bornheutter-Ferguson method : The Bornheutter-Ferguson method calculates the IBNR loss reserves as the product of the earned premium, an expected ultimate loss ratio, and a loss development factor that represents the expected percentage of the ultimate losses that have been incurred but not yet reported. The loss development factor equals one hundred percent less the expected percentage of losses that have thus far been reported, which is generally calculated as an average of the percentage of losses reported for comparable reporting periods of prior underwriting years. The expected ultimate loss ratio is generally determined in the same manner as in the loss ratio method.
Loss development method : The loss development method, also known as the chainladder or the link-ratio method, develops the IBNR loss reserves by multiplying the paid or reported losses by a loss development factor to estimate the ultimate losses, then subtracting the reported losses, consisting of paid losses and case loss reserves, to determine the IBNR loss reserves. The loss development factor is the reciprocal of the expected percentage of losses that have thus far been reported, which is generally calculated as an average of the percentage of losses reported for comparable reporting periods of prior underwriting years.
43
Frequency/severity method : The frequency/severity method calculates the IBNR loss reserves by separately projecting claim count and average cost per claim data on either a paid or incurred basis. It estimates the expected ultimate losses as the product of the ultimate number of claims that are expected to be reported and the expected average amount of these claims.
An annual loss reserve study is conducted by the Company's actuaries for each major line of business employing the methodologies as described above with the timing of such studies varying throughout the year. Additionally, a review of the emergence of actual losses relative to expectations for each line of business, generally derived from the annual reserve study, is conducted each quarter to determine whether the assumptions used in the reserving process continue to form a reasonable basis for the projection of liabilities for each product line. Such reviews may result in maintaining or revising assumptions regarding future loss development based on various quantitative and qualitative considerations. If actual loss activity differs from expectations, an upward or downward adjustment to loss reserves may occur. As time passes, estimated loss reserves for an underwriting year will be based more on historical loss activity and loss development patterns rather than on assumptions based on underwriters' input, pricing assumptions or industry experience.
The following discusses the method used for calculating the IBNR for each line of business and key assumptions used in applying the actuarial methods described.
Marine : Generally, two key assumptions are used by our actuaries in setting IBNR loss reserves for major products in this line of business. The first assumption is that our historical experience regarding paid and reported losses for each product where we have sufficient history can be relied on to predict future loss activity. The second assumption is that our underwriters' assessments as to potential loss exposures are reliable indicators of the level of our expected loss activity. The specific loss reserves for marine are then analyzed separately by product based on such assumptions, except where noted below, with the major products including marine liability, cargo, P&I, transport and bluewater hull.
The claims emergence patterns for various marine product lines vary substantially. Our largest marine product line is marine liability, which has one of the longer loss development patterns. Marine liability protects an insured's business from liability to third parties stemming from their marine-related operations, such as terminal operations, stevedoring and marina operations. Since marine liability claims generally involve a dispute as to the extent and amount of legal liability that our insured has to a third party, these claims tend to take a longer time to develop and settle. Other longer-tail marine product lines include P&I insurance, which provides coverage for third party liability as well as injury to crew for vessel operators, and transport insurance, which provides both property and third party liability on a primary basis to businesses such as port authorities, marine terminal operators and others engaged in the infrastructure of international transportation. Other marine product lines have considerably shorter periods in which losses develop and settle. Ocean cargo insurance, for example, provides physical damage coverage to goods in the course of transit by water, air or land. By their nature, cargo claims tend to be reported quickly as losses typically result from an obvious peril such as fire, theft or weather. Similarly, bluewater hull insurance provides coverage against physical damage to ocean-going vessels. Such claims for physical damage generally are discovered, reported and settled quickly. The Company currently has extensive experience for all of these products and thus the IBNR loss reserves for all of the marine products are determined using the key assumptions and actuarial methodologies described above. Prior to 2007, however, as discussed below, the Company did not have sufficient experience in the transport product line and instead used its hull and liability products loss development experience as a key assumption in setting the IBNR loss reserves for its transport product.
44
Property Casualty : The reserves for property and casualty are established separately by product with the major product being contractors' liability insurance. Other products include offshore energy, commercial middle markets, primary casualty and excess casualty. Our actuaries generally utilize two key assumptions in this line of business: first, that our historical loss development patterns are reasonable predictors of future loss patterns and second, that our claims personnel's assessment of our claims exposures and our underwriters' assessment of our expected losses are reliable indicators of our loss exposure. However, this line of business includes a number of newer products where there is insufficient Company historical experience to project loss reserves and/or loss development is sparse or erratic, which makes extrapolation techniques for those products extremely difficult to apply, and in those circumstances we typically rely more on industry data and our underwriters' input in setting assumptions for our IBNR loss reserves as opposed to historical loss development patterns. In addition, as discussed in more detail below with respect to construction defect reserves, our actuaries may take other market trends or events into account in setting IBNR loss reserves.
The substantial majority of the property and casualty loss reserves are for the contractors' liability business, which insures mostly general and artisan contractors. Contractor liability claims are categorized into two claim types: construction defect and other general liability. Other general liability claims typically derive from workplace accidents or from negligence alleged by third parties, and take a long time to report and settle. Construction defect claims involve the discovery of damage to buildings that was caused by latent construction defects. These claims take a very long time to report and to settle compared to other general liability claims. Since construction defect claims report much later than other contractor liability claims, they are analyzed separately in the annual loss reserve study.
We have extensive history in the contractors' liability business upon which to perform actuarial analyses and we use the key assumption noted above relating to our own historical experience as a reliable indicator of the future for this product. However, there is inherent uncertainty in the loss reserve estimation process for this line of business given both the long-tail nature of the liability claims and the continuing underwriting and coverage changes, claims handling and reserve changes, and legislative changes that have occurred over a several year period. Such factors are judgmentally taken into account in this line of business in specific periods. The underwriting and coverage changes include the migration to a non-admitted business from admitted business in 2003, which allowed us to exclude certain exposures previously permitted (for example, exposure to construction work performed prior to the policy inception), withdrawals from certain contractor classes previously underwritten and expansion into new states beginning in 2005. Claims changes include bringing the claim handling in-house in 1999 and changes in case reserving practices in 2003 and 2006. A California legislative change with respect to reserves and claim frequency for construction defect repairs, became effective July 1, 2002 with a sunset provision effective January 1, 2011. The law provides for an alternative dispute resolution system that attempts to involve all parties to a claim at an early stage. The legislation may impact claim severity, frequency and the length of settlement which may ultimately be different than historical loss development assumptions employed in our loss reserve process.
Most recently, in setting the IBNR loss reserves for construction defect claims, our actuaries have begun to consider a new qualitative factor based on their evolving concern with the recent decline in home values caused by the subprime home mortgage crisis and its possible impact on the frequency and severity of construction defect claims. As a result, our actuaries acknowledge this uncertainty and anticipate claims arising from alleged construction defects contributing to housing value declines on policies written on newly constructed homes in our portfolio. We believe our reserves remain adequate to address such potential exposure, but we can give no assurances with respect thereto.
Offshore energy provides physical damage coverage to offshore oil platforms along with offshore operations related to oil exploration and production. The significant offshore energy claims are generally caused by fire or storms, and thus tend to be large, infrequent, quickly reported, but occasionally not quickly settled because the damage is often extensive but not always immediately known.
The commercial middle markets or NAV PAC business consists of general liability, auto liability and property exposures for a variety of commercial middle market businesses, principally hospitality, manufacturing and garages. Commencing in 2007, our actuaries are segmenting and analyzing the components of the loss development for this business among the property, liability and auto exposures which had been previously combined.
45
Primary casualty insurance provides primary general liability coverage principally to corporations in the construction and manufacturing sector. Excess casualty insurance is purchased by corporations which seek higher limits of liability than are provided in their primary casualty policies. Neither product line has a significant amount of loss activity reported to date. Because we have limited historical experience in these products, the IBNR loss reserves for both of these products currently are established using the loss ratio method primarily based on our underwriters' input and industry loss experience.
Loss reserves include our European property business written by the U.K. Branch which was discontinued in 2008. We have limited loss history and rely primarily on assumptions based on underwriters' input and industry experience. In addition, loss reserves for aviation, property and assumed reinsurance business, in run-off since 1999, are periodically monitored and evaluated by claims and actuarial personnel.
Professional Liability : The professional liability policies mainly provide coverage on a claims-made basis mostly for a one-year period. The reserves for professional liability are analyzed separately by product with the major products being directors and officers ("D&O") liability coverage and errors and omissions ("E&O") liability coverage for lawyers and other professionals.
The losses for D&O business are generally very large and infrequent, and typically involve securities class actions. D&O claims report reasonably quickly, but may take several years to settle. While we have been writing D&O business since 2001, the limited claim history is generally insufficient to establish IBNR loss reserves using Company data. As a result, we principally employ assumptions based on industry experience coupled with input from its underwriters and its claims staff's assessment of potential exposure to establish IBNR loss reserves. Another key assumption with respect to establishing IBNR loss reserves for D&O business is that such industry experience is representative of our future potential loss development with respect to trends in class action activity, such as the impact of stock option backdating, laddering and, most recently, the subprime mortgage crisis. As time passes, for a given underwriting year, additional weight is given to assumptions relating to our actual experience and claims outstanding.
The E&O IBNR loss reserve process is similar to the process for D&O, with the exception of a particular book of business of the U.K. Branch written from 2004 through 2006. For the U.K. Branch E&O business, we assume the claims, while similar in nature to the claims in the U.S. E&O business, are larger, more frequent and have a longer loss development pattern. The IBNR loss reserves for the U.K. Branch E&O business are determined judgmentally after reviewing recent loss activity relative to the remaining in-force policy count and the loss activity for similar insureds.
Lloyd's Operations : Reserves for the Company's Lloyd's Operations are reviewed separately for the marine and professional liability lines by product. The major marine products are marine liability, offshore energy, cargo, specie and marine reinsurance, and the major products for professional liability are international D&O and international E&O.
The marine liability, offshore energy and cargo products and related loss exposures are similar in nature to that described for marine business above. Specie insurance provides property coverage for chattel, such as jewelry, fine art and cash in transit. Claims tend to be from theft or damage, quick to report and quick to settle. Marine reinsurance is a diversified global book of reinsurance, the majority of which consists of excess-of-loss reinsurance policies for which claims activity tends to be large and infrequent with loss development somewhat longer than for such products written on a direct basis. Marine reinsurance reinsures liability, cargo, hull and offshore energy exposures that are similar in nature to the marine business described above.
The process for establishing the IBNR loss reserves for the marine and professional liability lines of the Lloyd's Operations, and the assumptions used as part of this process, are similar in nature to the process employed by the Insurance Companies. Other business for the Lloyd's Operations include European property and inland marine products, each of which is a new line of business where we have limited loss history and rely primarily on assumptions based on our underwriters' input and industry loss experience.
46
The Lloyd's Operations products also include property coverages for engineering and construction projects and onshore energy business, which are substantially reinsured. Losses from engineering and construction projects tend to result from loss of use due to construction delays while losses from onshore energy business are usually caused by fires or explosions. Large losses tend to be catastrophic in nature and are heavily reinsured. IBNR loss reserves for attritional losses are established based on the Syndicate's extensive loss experience.
Sensitivity Analysis
We do not calculate a range of loss reserve estimates. We believe that ranges may not be a true reflection of the potential volatility between carried loss reserves and the ultimate settlement amount of losses incurred prior to the balance sheet date.
The actual losses may not emerge as expected, which would cause the ranges to expand or contract from year to year. The impact of these shifts in the ranges will be greater in lines with longer emergence patterns. The individual lines will also have greater variance than the range for the entire book of business. The boundaries of the reasonably likely ranges do not have a symmetrical relationship with our carried reserves and intentionally reflect a wider variation in the increases than for the decreases and, correspondingly, a wider deviation in the deficiency than in the redundancy.
Set forth below is a sensitivity analysis that estimates the effect on our net loss reserve position of using alternative expected loss ratios for the underwriting years 2002 to 2009 and alternative loss development factors for underwriting years 1997 to 2009 rather than those loss ratios and factors actually used in determining our best estimates at December 31, 2009. The analysis addresses each major line of business and underwriting year for which a material deviation to our overall reserve position is believed reasonably possible, and uses what we believe is a reasonably likely range of potential deviation for each line of business. There can be no assurance, however, that actual reserve development will be materially consistent with either the original or the adjusted expected loss ratios or loss development factor assumptions, or with other assumptions made in the reserving process.
For the selected alternative expected loss ratios, our actuaries observed the range of ultimate loss ratios recorded for the underwriting years 2002 to 2009 for each major line of business at December 31, 2009.
47
The reasonably likely ranges of potential deviation in the loss ratios for each line of business for the 2002 to 2009 underwriting years expressed in loss ratio points are as follows:
Reasonably likely loss ratio point variances
| Decrease | Increase | |||||||
| ||||||||
Insurance Companies: | ||||||||
Marine | 5 | % | 6 | % | ||||
Property Casualty | 7 | % | 14 | % | ||||
Professional Liability | 13 | % | 16 | % | ||||
Lloyd's Operations | 7 | % | 12 | % | ||||
For the loss development factor variance, our actuaries employed a standard technique which is based on the historical development factors observed for each line of business from the paid and incurred loss development triangles with the latest evaluation at December 31, 2009. The historical factors are used to generate alternative outcomes which could arise in the ultimate development due to the random variability inherent in future development. The alternative outcomes are generated by a stochastic simulation. The ranges may contract or expand if future development deviates from historical experience.
The reasonably likely ranges of potential deviations in the aggregate or overall loss development factors applicable to the total of all underwriting years for each line of business are as follows:
Reasonably likely ultimate loss development factor variances
| Decrease | Increase | |||||||
| ||||||||
Insurance Companies: | ||||||||
Marine | 9 | % | 12 | % | ||||
Property Casualty | 14 | % | 16 | % | ||||
Professional Liability | 27 | % | 30 | % | ||||
Lloyd's Operations | 14 | % | 15 | % | ||||
Such sensitivity analysis was performed in the aggregate for all products in each line of business. The use of aggregate data was considered more stable and reliable compared to a product-by-product analysis. We cannot assure, however, that such use of aggregate data will provide a more accurate range of the actual variations in loss development. The sensitivity analysis uses loss ratios for the 2002 to 2009 underwriting years, which are believed to be more representative compared to years prior to 2002 given our evolving mix of business, product changes and other factors. There can be no assurances, however, that the use of such recent history is more predictive of actual development as compared to employing longer periods of history. In addition, while the net loss reserves include the net loss reserves for asbestos exposures, such amounts were excluded from the sensitivity analysis given the nature of how such reserves are established by the Company. While we believe such net reserves are adequate, we cannot assure that material loss development may not arise in the future from asbestos losses given the complex nature of such exposures.
48
The total Company range amounts below were determined by aggregating the reasonably likely range amounts for each line of business assuming that the variances in the lines of business are uncorrelated to each other. Such amounts may not be representative of the actual aggregate favorable or unfavorable loss development amounts that may occur over time.
| Total | Reasonably Likely Range of Deviation | |||||||||||||||||||
| Net Loss | Redundancy | Deficiency | ||||||||||||||||||
| Reserve | Amount | % | Amount | % | ||||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Insurance Companies | ||||||||||||||||||||
Marine | $ | 213,646 | $ | 8,546 | 4 | % | $ | 12,819 | 6 | % | ||||||||||
Property Casualty | 486,412 | 34,049 | 7 | % | 38,913 | 8 | % | |||||||||||||
Professional Liability | 107,217 | 13,938 | 13 | % | 15,010 | 14 | % | |||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Total Insurance Companies | 807,275 | 56,533 | 7 | % | 66,742 | 8 | % | |||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Total Lloyd's Operations | 305,659 | 21,396 | 7 | % | 21,396 | 7 | % | |||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Total Company | $ | 1,112,934 | $ | 77,929 | 7 | % | $ | 88,138 | 8 | % | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Increase (decrease) to net income | ||||||||||||||||||||
Amount | $ | 50,654 | $ | (57,290 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Per Share (1) | $ | 2.92 | $ | (3.31 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| (1) | Used 17.3 million average diluted shares outstanding for the year ended December 31, 2009. |
Reinsurance Recoverables. Reinsurance recoverables are established for the portion of the loss reserves that are ceded to reinsurers. Reinsurance recoverables are determined based upon the terms and conditions of reinsurance contracts which could be subject to interpretations that differ from our own based on judicial theories of liability. In addition, we bear credit risk with respect to our reinsurers which can be significant considering that certain of the reserves remain outstanding for an extended period of time. We are required to pay losses even if a reinsurer fails to meet its obligations under the applicable reinsurance agreement. Additional information regarding our reinsurance recoverables can be found in the "Business-Reinsurance Recoverables" section and Note 6, Reinsurance , to our consolidated financial statements, both included herein.
Written and Unearned Premium. Written premium is recorded based on the insurance policies that have been reported to us and the policies that have been written by agents but not yet reported to us. We must estimate the amount of written premium not yet reported based on judgments relative to current and historical trends of the business being written. Such estimates are regularly reviewed and updated and any resulting adjustments are included in the current year's results. An unearned premium reserve is established to reflect the unexpired portion of each policy at the financial reporting date. Reinsurance reinstatement premium is earned in the period in which the event occurred which created the need to record the reinstatement premium. Additional information regarding our written and unearned premium can be found in Note 1, Organization and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies , and Note 6, Reinsurance , to our consolidated financial statements, both included herein.
Substantially all of our business is placed through agents and brokers. Since the vast majority of our gross written premiums are primary or direct, as opposed to assumed, the delays in reporting assumed premiums generally do not have a significant effect on our financial statements, since we record estimates for both unreported direct and assumed premium. We also record the ceded portion of the estimated gross written premium and related acquisition costs. The earned gross, ceded and net premiums are calculated based on our earning methodology which is generally pro-rata over the policy period. Losses are also recorded in relation to the earned premium. The estimate for losses incurred on the estimated premium is based on an actuarial calculation consistent with the methodology used to determine incurred but not reported loss reserves for reported premiums.
49
A portion of our premium is estimated for unreported premium, mostly for the marine business written by our U.K. Branch and Lloyd's Operations. We generally do not experience any significant backlog in processing premiums. Such premium estimates are generally based on submission data received from brokers and agents and recorded when the insurance policy or reinsurance contract is written or bound. The estimates are regularly reviewed and updated taking into account the premium received to date versus the estimate and the age of the estimate. To the extent that the actual premium varies from the estimates, the difference, along with the related loss reserves and underwriting expenses, is recorded in current operations.
Deferred Tax Assets. We apply the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes whereby deferred assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax basis. In assessing the realization of deferred tax assets, management considers whether it is more likely than not that the deferred tax assets will be realized. Additional information regarding our deferred tax assets can be found in Note 1, Organization and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies , and Note 7, Income Taxes , to our consolidated financial statements, both included herein.
Impairment of Invested Assets. Management regularly reviews our fixed maturity and equity securities portfolios to evaluate the necessity of recording impairment losses for other-than-temporary declines in the fair value of investments.
In the first quarter of 2009, we adopted accounting guidance relating to the recognition and presentation of other-than-temporary impairments ("OTTI") on fixed maturity securities. When assessing whether the amortized cost basis of a fixed maturity security will be recovered, we compare the present value of cash flows expected to be collected to the current book value. Any shortfalls of the present value of the cash flows expected to be collected in relation to the amortized cost basis is considered the credit loss portion of OTTI losses and is recognized in earnings. All non-credit losses are recognized as changes in OTTI losses within Other Comprehensive Income ("OCI"). Prior to 2009, when a fixed maturity security in our investment portfolio had an unrealized loss that was deemed to be other-than-temporary, we wrote the security down to fair value through a charge to operations.
For equity securities, in general, we focus our attention on those securities whose fair value was less than 80% of their cost for six or more consecutive months. If warranted as the result of conditions relating to a particular security, we will focus on a significant decline in fair value regardless of the time period involved. Factors considered in evaluating potential impairment include, but are not limited to, the current fair value as compared to cost of the security, the length of time the investment has been below cost and by how much. If an equity security is deemed to be other-than-temporarily impaired, the cost is written down to fair value with the loss recognized in earnings.
For equity securities, we consider our intent to hold securities as part of the process of evaluating whether a decline in fair value represents an other-than-temporary decline in value. For fixed maturity securities, we consider our intent to sell a security and whether it is more likely than not that we will be required to sell a security before the anticipated recovery as part of the process of evaluating whether a security's unrealized loss represents an other-than-temporary decline. Our ability to hold such securities is supported by sufficient cash flow from its operations and from maturities within its investment portfolio in order to meet its claims payments and other disbursement obligations arising from its underwriting operations without selling such investments. With respect to securities where the decline in value is determined to be temporary and the security's value is not written down, a subsequent decision may be made to sell that security and realize a loss. Subsequent decisions on security sales are made within the context of overall risk monitoring, changing information and market conditions.
50
Day to day management of our investment portfolio is outsourced to third party investment managers. While these investment managers may, at a given point in time, believe that the preferred course of action is to hold securities with unrealized losses that are considered temporary until such losses are recovered, the dynamic nature of the portfolio management may result in a subsequent decision to sell the security and realize the loss based upon a change in market and other factors described above. We believe that subsequent decisions to sell such securities are consistent with the classification of our portfolio as available-for-sale. Investment managers are required to notify management of rating agency downgrades of securities in their portfolios as well as any potential investment valuation issues at the end of each quarter. Investment managers are also required to notify management, and receive approval, prior to the execution of a transaction or series of related transactions that may result in a realized loss above a certain threshold. Additionally, investment managers are required to notify management, and receive approval, prior to the execution of a transaction or series of related transactions that may result in any realized loss up until a certain period beyond the close of a quarterly accounting period.
Accounting for Lloyd's Results. We record Syndicate 1221's assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses under U.S. GAAP. At the end of the Lloyd's three-year period for determining underwriting results for an account year, the syndicate will close the account year by reinsuring outstanding claims on that account year with the participants for the account's next underwriting year. The amount to close an underwriting year into the next year is referred to as the reinsurance to close ("RITC"). The RITC transaction, recorded in the fourth quarter, does not result in any gain or loss. Additional information regarding our accounting for Lloyd's results can be found in Note 1, Organization and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies , to our consolidated financial statements, included herein.
Results of Operations
The following is a discussion and analysis of our consolidated and segment results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007. All earnings per share data is presented on a per diluted share basis.
Summary
Net income for 2009, 2008 and 2007 was $63.2 million or $3.65 per diluted share, $51.7 million or $3.04 per diluted share and $95.6 million or $5.62 per diluted share, respectively. The 2008 year was adversely impacted by Hurricanes Gustav and Ike, reducing net income by $19.1 million and diluted earnings per share by $1.12.
Consolidated stockholders' equity increased 16.3% to $801.5 million or $47.58 per share at December 31, 2009 compared to $689.3 million or $40.89 per share at December 31, 2008. The increase was primarily due to 2009 net income of $63.2 million and $46.0 million of after-tax unrealized gains in 2009 within our investment portfolio.
Cash flow from operations was $103.9 million, $245.3 million and $284.6 million in 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively. The decline in cash flow from operations in 2009 compared to 2008 was primarily a result of an increase in losses and LAE paid for claims of $82.4 million. Net investment income decreased 1.4% in 2009 to $75.5 million compared to 2008 as a result of lower investment yields partially offset by an increase in invested assets. Net investment income increased 8.3% in 2008 to $76.6 million compared to 2007 as the result of the increase in invested assets partially offset by lower investment yields. The pre-tax investment yield was 3.8%, 4.1% and 4.4% in 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
51
2009 Results
2009 net income of $63.2 million increased $11.5 million compared to 2008 primarily as a result of a decrease in net other-than-temporary impairment losses recognized in earnings of $25.1 million to $11.9 million in 2009 compared to $37.0 million in 2008. Underwriting profit for 2009 declined by $19.8 million to $19.5 million compared to $39.3 million in 2008. The decline in the underwriting profit was primarily due to the recording of net redundancies of prior year loss reserves of $8.9 million in 2009 versus $50.7 million in 2008, a decline of $41.8 million. In addition, we recorded a $9.3 million offshore energy loss net of reinstatement premiums resulting from a fire at a mobile offshore drilling unit.
2008 Results
The 2008 results of operations were adversely impacted by hurricane activity and net realized losses. Hurricanes Gustav and Ike reduced 2008 net income by $19.1 million and earnings per share by $1.12. The combined loss and expense ratio was increased by an aggregate 4.3 ratio points for such losses and are inclusive of reinsurance recoveries and related costs for reinsurance reinstatement premiums. Excluding these effects, the underwriting results benefited from increased net premium revenues despite continuing softening market conditions, and the recording of a net redundancy of prior years' loss reserves of $50.7 million, or $1.94 per share, which reduced the 2008 combined ratio of 93.8% by 7.9 loss ratio points.
Net realized losses were $38.3 million in 2008 compared to net realized gains of $2.0 million in 2007. The 2008 net realized losses include provisions of $37.0 million for declines in the market value of securities which were considered to be other-than-temporary. These provisions reduced 2008 net income by $24.1 million and earnings per share by $1.42 per share.
2007 Results
The 2007 results of operations reflect improved financial performance compared to 2006 due to a combination of improved underwriting results and growth in investment income. The underwriting results benefited from increased net premium revenues despite continuing softening market conditions, and the recording of a net redundancy of prior years' loss reserves of $47.0 million, or $1.80 per share, which reduced the 2007 combined ratio of 87.5% by 7.8 loss ratio points.
52
Revenues
The following table sets forth our gross and net written premium and net earned premium by segment and line of business for the periods indicated:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross | Net | Net | Gross | Net | Net | Gross | Net | Net | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Written | Written | Earned | Written | Written | Earned | Written | Written | Earned | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Premiums | % | Premiums | Premiums | Premiums | % | Premiums | Premiums | Premiums | % | Premiums | Premiums | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Insurance Companies: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Marine | $ | 241,438 | 23.1 | % | $ | 171,289 | $ | 157,534 | $ | 248,080 | 22.9 | % | $ | 147,569 | $ | 132,005 | $ | 227,175 | 21.2 | % | $ | 117,294 | $ | 112,370 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Property Casualty | 352,285 | 33.7 | % | 227,234 | 246,143 | 405,062 | 37.3 | % | 261,322 | 273,977 | 447,615 | 41.8 | % | 301,607 | 275,937 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Professional Liability | 137,053 | 13.1 | % | 79,150 | 75,444 | 109,048 | 10.1 | % | 63,797 | 57,316 | 99,556 | 9.3 | % | 59,117 | 55,149 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Insurance Cos. Total | 730,776 | 69.9 | % | 477,673 | 479,121 | 762,190 | 70.3 | % | 472,688 | 463,298 | 774,346 | 72.3 | % | 478,018 | 443,456 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lloyd's Operations: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Marine | 191,959 | 18.4 | % | 156,153 | 142,958 | 192,568 | 17.7 | % | 132,788 | 126,126 | 175,567 | 16.4 | % | 110,577 | 111,380 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Property Casualty | 78,151 | 7.5 | % | 45,097 | 39,330 | 91,292 | 8.4 | % | 32,735 | 32,644 | 86,513 | 8.1 | % | 33,852 | 29,482 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Professional Liability | 44,032 | 4.2 | % | 22,332 | 21,954 | 38,872 | 3.6 | % | 23,404 | 21,908 | 34,281 | 3.2 | % | 23,349 | 17,659 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lloyd's Ops. Total | 314,142 | 30.1 | % | 223,582 | 204,242 | 322,732 | 29.7 | % | 188,927 | 180,678 | 296,361 | 27.7 | % | 167,778 | 158,521 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 1,044,918 | 100.0 | % | $ | 701,255 | $ | 683,363 | $ | 1,084,922 | 100.0 | % | $ | 661,615 | $ | 643,976 | $ | 1,070,707 | 100.0 | % | $ | 645,795 | $ | 601,977 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
53
Gross Written Premiums
The premium rate increases or decreases as noted below for marine, property casualty and professional liability are calculated primarily by comparing premium amounts on policies that have renewed. The premiums are judgmentally adjusted for exposure factors when deemed significant and sometimes represent an aggregation of several lines of business. The rate change calculations provide a pricing trend and are not meant to be a precise analysis. The calculation can also be affected quarter by quarter depending on the particular policies and the number of policies that renew during that period. Due to market conditions, these rate changes may or may not apply to new business which potentially may be more competitively priced compared to renewal business.
Insurance Companies' Gross Written Premiums
Marine Premiums. The gross written premiums by year, including the line of business' gross written premiums as a percentage of the total gross written premiums, consisted of the following:
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Marine liability | $ | 83,915 | 34 | % | $ | 82,991 | 32 | % | $ | 84,270 | 37 | % | ||||||||||||
Inland marine | 28,573 | 12 | % | 23,914 | 10 | % | 12,154 | 5 | % | |||||||||||||||
Cargo | 26,636 | 11 | % | 34,202 | 14 | % | 30,282 | 13 | % | |||||||||||||||
P&I | 25,361 | 11 | % | 28,935 | 12 | % | 26,312 | 12 | % | |||||||||||||||
Transport | 21,527 | 9 | % | 23,013 | 9 | % | 19,587 | 9 | % | |||||||||||||||
Bluewater hull | 19,691 | 8 | % | 17,234 | 7 | % | 23,508 | 10 | % | |||||||||||||||
Craft/Fishing vessel | 19,758 | 8 | % | 16,545 | 7 | % | 15,986 | 7 | % | |||||||||||||||
Other | 15,977 | 7 | % | 21,246 | 9 | % | 15,076 | 7 | % | |||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 241,438 | 100 | % | $ | 248,080 | 100 | % | $ | 227,175 | 100 | % | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
The marine gross written premiums for 2009 decreased 2.7% to $241.4 million compared to 2008 due to declining premium in our cargo, war and P&I businesses due to increased competitive market conditions. The average marine renewal premium rates during 2009 increased approximately 2%. The marine gross written premiums for 2008 increased 9.2% to $248.1 million compared to 2007 reflecting new business partially offset by flattening or declining premium in several classes of business due to increased competitive market conditions. The average marine renewal premium rates during 2008 were flat.
Property Casualty Premiums. The gross written premiums by year, including the line of business' gross written premiums as a percentage of the total gross written premiums, consisted of the following:
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Construction liability | $ | 90,627 | 26 | % | $ | 147,880 | 36 | % | $ | 179,633 | 40 | % | ||||||||||||
Commercial umbrella | 72,509 | 21 | % | 63,977 | 16 | % | 57,371 | 13 | % | |||||||||||||||
Offshore energy | 47,368 | 13 | % | 56,989 | 14 | % | 51,627 | 12 | % | |||||||||||||||
Primary E&S | 23,783 | 7 | % | 35,744 | 9 | % | 50,185 | 11 | % | |||||||||||||||
Other | 117,998 | 33 | % | 100,472 | 25 | % | 108,799 | 24 | % | |||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 352,285 | 100 | % | $ | 405,062 | 100 | % | $ | 447,615 | 100 | % | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 2009 property casualty gross written premiums decreased 13.0% to $352.3 million when compared to 2008 reflecting weakening economic conditions that have significantly reduced demand for construction liability, particularly in the western United States, as well as primary excess and surplus insurance. The construction liability line has also seen significant increases in the level of competition from new entrants. Our offshore energy line declined as we wrote very little Gulf of Mexico wind business in 2009 as the terms and conditions were not sufficient and world wide drilling activity slowed. Partially offsetting these declines was an increase in gross written premiums for our commercial umbrella line and our retail umbrella line which was introduced in 2009. Our NavTech and excess casualty lines saw average renewal rate increases of approximately 8% and 2%, respectively, whereas our contractors' liability and NavPac lines saw average renewal rate decreases of 2% and 4%, respectively. The 2008 property casualty gross written premiums decreased 9.5% to $405.1 million when compared to 2007 reflecting declines across most lines of business due to negative renewal rate changes and the housing market slowdown, which was most pronounced in the construction liability line.
54
Professional Liability Premiums. The gross written premiums by year, including the line of business' gross written premiums as a percentage of the total gross written premiums, consisted of the following:
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
D&O (public and private) | $ | 99,601 | 73 | % | $ | 75,010 | 69 | % | $ | 67,973 | 68 | % | ||||||||||||
Errors and omissions | 32,129 | 23 | % | 28,097 | 26 | % | 24,515 | 25 | % | |||||||||||||||
Architects and engineers | 5,323 | 4 | % | 5,941 | 5 | % | 7,068 | 7 | % | |||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 137,053 | 100 | % | $ | 109,048 | 100 | % | $ | 99,556 | 100 | % | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
The professional liability gross written premiums increased 25.7% to $137.1 million in 2009 compared to 2008 reflecting continued growth and the expansion of our directors and officers business. Partially offsetting the growth has been a reduction in lawyers business within the errors and omissions classification as we have been in the process of re-underwriting that line and focusing more on other segments, such as miscellaneous professional liability. Average 2009 renewal premium rates for this business increased approximately 2% in 2009 compared to 2008. The professional liability gross written premiums increased 9.5% to $109.0 million in 2008 compared to 2007 due to the expansion of our professional liability business and an emerging flight to quality that occurred in the latter part of the year. Average 2008 renewal premium rates for this business decreased approximately 4% in 2008 compared to 2007.
Lloyd's Operations' Gross Written Premiums
Marine Premiums. The gross written premiums by year, including the line of business' gross written premiums as a percentage of the total gross written premiums, consisted of the following:
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cargo and specie | $ | 92,139 | 48 | % | $ | 92,789 | 47 | % | $ | 87,412 | 50 | % | ||||||||||||
Marine liability | 51,204 | 27 | % | 58,886 | 31 | % | 48,172 | 27 | % | |||||||||||||||
Assumed reinsurance | 19,756 | 10 | % | 17,078 | 9 | % | 24,280 | 14 | % | |||||||||||||||
Hull | 18,697 | 10 | % | 16,416 | 9 | % | 13,218 | 8 | % | |||||||||||||||
War | 10,163 | 5 | % | 7,399 | 4 | % | 2,485 | 1 | % | |||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 191,959 | 100 | % | $ | 192,568 | 100 | % | $ | 175,567 | 100 | % | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
The overall 2009 Lloyd's marine gross written premiums of $192.0 million were flat compared to 2008. There were increases in most lines of business which were offset by decreases in marine liability and cargo lines. The 2008 increase in Lloyd's marine gross written premiums of 9.7% compared to 2007 resulted from new business, particularly in the marine liability class. The average renewal premium rate increased approximately 8.9% in 2009 and decreased 5.1% in 2008 from the previous year, respectively.
55
Property Casualty Premiums. The gross written premiums by year, including the line of business' gross written premiums as a percentage of the total gross written premiums, consisted of the following:
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Offshore energy | $ | 34,469 | 43 | % | $ | 51,073 | 56 | % | $ | 49,649 | 57 | % | ||||||||||||
Onshore energy | 14,055 | 18 | % | 12,726 | 14 | % | 9,151 | 11 | % | |||||||||||||||
Engineering & construction | 18,383 | 24 | % | 21,036 | 23 | % | 18,551 | 21 | % | |||||||||||||||
Bloodstock | 7,726 | 10 | % | - | 0 | % | - | 0 | % | |||||||||||||||
Property | (76 | ) | 0 | % | 5,631 | 6 | % | 9,162 | 11 | % | ||||||||||||||
US Casualty | 3,594 | 5 | % | 826 | 1 | % | - | 0 | % | |||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 78,151 | 100 | % | $ | 91,292 | 100 | % | $ | 86,513 | 100 | % | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 2009 Lloyd's property casualty gross written premiums of $78.2 million decreased 14.4% compared to 2008 due to a decline in our offshore energy and engineering and construction lines as well as the cessation of writing our property line. We began writing Bloodstock (animal mortality) business during 2009 by participating in a facility originated by another Lloyd's syndicate. The 2008 gross written premiums of $91.3 million increased 5.5% compared to 2007 due to increases in all of our NavTech lines. Average premium renewal rates in our NavTech lines were a 10.1% increase in 2009 and a 10.0% decrease in 2008 compared to the previous year, respectively.
Professional Liability Premiums. The gross written premiums by year, including the line of business' gross written premiums as a percentage of the total gross written premiums, consisted of the following:
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
D&O (public and private) | $ | 26,776 | 61 | % | $ | 15,845 | 41 | % | $ | 16,511 | 48 | % | ||||||||||||
E&O | 17,256 | 39 | % | 23,027 | 59 | % | 17,770 | 52 | % | |||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 44,032 | 100 | % | $ | 38,872 | 100 | % | $ | 34,281 | 100 | % | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Our Lloyd's Operations commenced writing professional liability business during the second quarter of 2005. The 2009 and 2008 Lloyd's professional liability gross written premiums increased 13.3% and 13.4% to $44.0 million and $38.9 million, respectively, compared to the respective prior year, due to continued expansion and geographic diversification of the book of business. We added a team at Lloyd's at the end of 2008 to write excess D&O business. In addition, during 2009 we began writing professional liability business from our office in Stockholm, Sweden.
Ceded Written Premium In the ordinary course of business, we reinsure certain insurance risks with unaffiliated insurance companies for the purpose of limiting our maximum loss exposure, protecting against catastrophic losses, and maintaining desired ratios of net premiums written to statutory surplus. The relationship of ceded to written premiums varies based upon the types of business written and whether the business is written by the Insurance Companies or the Lloyd's Operations.
56
The following table sets forth our ceded written premium by segment and major line of business for the periods indicated:
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| % of | % of | % of | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ceded | Gross | Ceded | Gross | Ceded | Gross | |||||||||||||||||||
| Written | Written | Written | Written | Written | Written | |||||||||||||||||||
| Premiums | Premiums | Premiums | Premiums | Premiums | Premiums | |||||||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Insurance Companies | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Marine | $ | 70,149 | 29.1 | % | $ | 100,511 | 40.5 | % | $ | 109,881 | 48.4 | % | ||||||||||||
Property Casualty | 125,051 | 35.5 | % | 143,740 | 35.5 | % | 146,008 | 32.6 | % | |||||||||||||||
Professional Liability | 57,903 | 42.2 | % | 45,251 | 41.5 | % | 40,439 | 40.6 | % | |||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Subtotal | 253,103 | 34.6 | % | 289,502 | 38.0 | % | 296,328 | 38.3 | % | |||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lloyd's Operations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Marine | 35,806 | 18.7 | % | 59,780 | 31.0 | % | 64,990 | 37.0 | % | |||||||||||||||
Property Casualty | 33,054 | 42.3 | % | 58,557 | 64.1 | % | 52,661 | 60.9 | % | |||||||||||||||
Professional Liability | 21,700 | 49.3 | % | 15,468 | 39.8 | % | 10,932 | 31.9 | % | |||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Subtotal | 90,560 | 28.8 | % | 133,805 | 41.5 | % | 128,583 | 43.4 | % | |||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 343,663 | 32.9 | % | $ | 423,307 | 39.0 | % | $ | 424,911 | 39.7 | % | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
The percentage of total ceded written premiums to total gross written premium in 2009 was 32.9% compared to 39.0% in 2008 and 39.7% in 2007. The Insurance Companies' and Lloyd's Operations 2008 ceded written premiums includes $7.2 million and $5.0 million, respectively, of reinstatement premiums related to the losses from Hurricanes Gustav and Ike. Excluding the effect of reinstatement premiums for the 2008 Hurricanes losses, the ratio of ceded written premium to gross written premium was 38.4%. The declines in the ratio of ceded written premiums to gross written premiums in 2009 compared to 2008 was due to the a reduction in the amount of marine and energy quota share reinsurance purchased for both the Insurance Companies and Lloyd's Operations in 2009 as well as the impact of the $12.2 million of reinstatement premiums recognized in 2008 relating to the 2008 Hurricanes.
Net Written Premiums The 2009 net written premiums increased 6.0% compared to 2008 primarily due to the aforementioned reduction in the amount of marine and energy quota share reinsurance purchased in 2009. The 2009 increase was 4.1% compared to 2008 when excluding the $12.2 million of ceded reinstatement premiums resulting from the 2008 Hurricanes. The 2008 net written premiums increased 2.4% compared to 2007. The 2008 increase was 4.3% compared to 2007 when excluding the $12.2 million of ceded reinstatement premiums resulting from the 2008 Hurricanes.
Net Earned Premiums Net earned premiums increased 6.1% in 2009 compared to 2008 and increased 7.0% in 2008 compared to 2007. The 2009 and 2008 net earned premium increases reflect the changes in written premiums discussed above. The 2008 net earned premium was reduced by $12.2 million of reinstatement premium as a result of the losses from the 2008 Hurricanes. Excluding the effects of ceded reinstatement premiums as a result of the 2008 Hurricanes, net earned premium increased 4.1% in 2009 compared to 2008 and 9.0% in 2008 compared to 2007.
57
Commission Income Commission income from unaffiliated business decreased 91.4% to $0.1 million in 2009 compared to 2008 and decreased 42.1% to $1.0 million in 2008 compared to $1.7 million in 2007. Beginning with the 2006 underwriting year, there are no longer any unaffiliated marine pool insurance companies and we purchased the Syndicate 1221 minority interest, therefore any profit commission therefore results from the run-off of underwriting years prior to 2006.
Net Investment Income Net investment income decreased 1.4% in 2009 to $75.5 million compared to 2008 as a result of lower investment yields partially offset by an increase in invested assets resulting from positive cash flow from operations. Net investment income increased 8.3% in 2008 to $76.6 million compared to 2007 as the result of the increase in invested assets resulting from positive cash flow from operations partially offset by lower investment yields. The pre-tax investment yield was 3.8%, 4.1% and 4.4% in 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively. See the "Investments" section below for additional information regarding our net investment income.
Net Other-Than-Temporary Impairment Losses Recognized in Earnings
Our net other-than-temporary impairment losses recognized in earnings for the periods indicated were as follows:
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Fixed maturities | $ | (3,101 | ) | $ | (8,604 | ) | $ | - | ||||
Equity securities | (8,776 | ) | (28,441 | ) | (655 | ) | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net other-than-temporary impairment losses recognized in earnings | $ | (11,877 | ) | $ | (37,045 | ) | $ | (655 | ) | |||
| ||||||||||||
The 2009 other-than-temporary impairments were primarily related to additional impairments on equity securities that were impaired in 2008 as well as impairments on residential mortgage-backed securities. The after-tax effects of net other-than-temporary impairment losses recognized in earnings on the 2009 and 2008 net income were $7.8 million or $0.45 per diluted share and $24.1 million or $1.42 per share, respectively. In 2009, we recognized in earnings OTTI losses of $2.5 million and $0.08 million related to non-agency mortgage and asset-backed securities, respectively. In 2009, we recognized in earnings OTTI losses of $8.8 million on 56 common stocks resulting from additional impairments on equity securities that were impaired in 2008. In addition, in 2009 we recognized in earnings OTTI losses of $0.6 million on 2 corporate bonds.
The 2008 other-than-temporary impairments were primarily due to equity impairments where the market value of the security was less than 80% of the book value for six consecutive months resulting from the significant overall market declines in the second half of 2008. In addition, 2008 also included impairments on residential mortgage-backed securities. During 2008, we identified equity securities with fair value of $34.4 million which were considered to be other-than-temporarily impaired. Consequently, the cost of such securities was written down to fair value and we recognized realized losses of $28.4 million. The equity impairments include $8.6 million in write-downs to fair value for various broad based ETFs and mutual funds where the fair value was less than 80% of the book value. During 2008, we identified fixed maturity securities with fair value of $7.4 million which were considered to be other-than-temporarily impaired. Consequently, the cost of such securities was written down to fair value and we recognized realized losses of $8.6 million.
58
The significant inputs used to measure the amount of credit loss recognized in earnings were actual delinquency rates, default probability assumptions, severity assumptions and prepayment assumptions. Projected losses are a function of both loss severity and probability of default. Default probability and severity assumptions differ based on property type, vintage and the stress of the collateral. We do not intend to sell any of these securities and it is more likely than not that we will not be required sell these securities before the recovery of the amortized cost basis.
Net Realized Gains (Losses)
Our realized gains and losses for the periods indicated were as follows:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Fixed maturities: | ||||||||||||
Gains | $ | 18,312 | $ | 3,650 | $ | 1,320 | ||||||
(Losses) | (9,676 | ) | (1,670 | ) | (1,749 | ) | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
| 8,636 | 1,980 | (429 | ) | ||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Equity securities: | ||||||||||||
Gains | 2,110 | 720 | 3,626 | |||||||||
(Losses) | (1,529 | ) | (3,954 | ) | (536 | ) | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
| 581 | (3,234 | ) | 3,090 | ||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net realized gains (losses) | $ | 9,217 | $ | (1,254 | ) | $ | 2,661 | |||||
| ||||||||||||
Pre-tax net income included $9.2 million of net realized gains for 2009 compared to $1.3 million of net realized losses for 2008 and net realized gains of $2.7 million for 2007. On an after-tax basis, the net realized gains for 2009 were $5.9 million or $0.34 per diluted share compared to the net realized losses of $0.8 million or $0.05 per diluted share for 2008 and the net realized gains of $1.7 million or $0.10 per diluted share for 2007. Net realized gains and losses are generated from the sale of securities in the normal course of management of the investment portfolio.
Other Income/(Expense ) Other income/(expense) for 2009, 2008 and 2007 consisted primarily of foreign exchange gains and losses from our Lloyd's Operations and inspection fees related to our specialty insurance business.
Operating Expenses
Net Losses and Loss Adjustment Expenses Incurred
The ratios of net losses and loss adjustment expenses to net earned premiums (loss ratios) were 63.8%, 61.0% and 56.6% in 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively. The 2009 loss ratio of 63.8% was favorably impacted by 1.3 loss ratio points resulting from an $8.9 million net redundancy of prior years' loss reserves. The 2008 loss ratio of 61.0% was favorably impacted by 7.9 loss ratio points resulting from the $50.7 million net redundancy of prior years' loss reserves and adversely impacted by 3.7 loss ratio points related to the 2008 Hurricanes. The result of underwriting losses caused by Hurricanes Gustav and Ike of approximately $29.3 million, including $12.2 million of reinstatement costs, increased the 2008 combined ratio by 4.3 ratio points. The 2007 loss ratio of 56.6% was favorably impacted by 7.8 loss ratio points resulting from the $47.0 million net redundancy of prior year loss reserves. The 2007 loss ratio also included 0.9 loss ratio points for the U.K. flood losses in the Insurance Companies' U.K. Branch's property business and the Lloyd's marine cargo business.
59
During 2008 and 2007, reserve reductions resulting from periodic reviews of the 2005 Hurricanes' exposures reduced gross losses incurred by $12.3 million and $29.3 million, respectively. The reductions to the 2005 Hurricanes gross reserve estimates resulted in reductions of $1.0 million and $1.9 million to our 2008 and 2007 net loss incurred estimates, respectively, and reductions of $0.8 million and $0.7 million to our 2008 and 2007 reinstatement cost estimates, respectively. As a result of these reviews in 2007, we also reallocated our net retention for these events between our Insurance Companies and Lloyd's operations and the result was to increase the Insurance Companies loss incurred by $1.5 million and decrease the Lloyd's loss incurred by $3.4 million. During 2009 there was a minor increase in the gross and net losses incurred for the 2005 Hurricanes of $0.7 million and $0.1 million, respectively.
Prior Year Reserve Redundancies/Deficiencies
As part of our regular review of prior reserves, our actuaries may determine, based on their judgment, that certain assumptions made in the reserving process in prior years may need to be revised to reflect various factors, likely including the availability of additional information. Based on their reserve analyses, our actuaries may make corresponding reserve adjustments.
Prior year reserve redundancies of $8.9 million, $50.7 million and $47.0 million net of reinsurance were recorded in 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively, as discussed below. The relevant factors that may have a significant impact on the establishment and adjustment of loss and LAE reserves can vary by line of business and from period to period.
To the extent that reserves are deficient or redundant, the amount of such deficiency or redundancy is recorded as a charge or credit to earnings in the period in which the deficiency or redundancy is identified based on the information that is available at that time.
The segment and line of business breakdowns of prior period net reserve deficiencies (redundancies) were as follows:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||
Insurance Companies | ||||||||||||
Marine | $ | 11,893 | $ | (5,298 | ) | $ | (11,595 | ) | ||||
Property Casualty | (35,658 | ) | (33,065 | ) | (11,836 | ) | ||||||
Professional Liability | 20,686 | (3,559 | ) | (10,365 | ) | |||||||
| ||||||||||||
Insurance Companies | $ | (3,079 | ) | $ | (41,922 | ) | $ | (33,796 | ) | |||
Lloyd's Operations | (5,862 | ) | (8,824 | ) | (13,213 | ) | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
Total | $ | (8,941 | ) | $ | (50,746 | ) | $ | (47,009 | ) | |||
| ||||||||||||
Following is a discussion of relevant factors impacting our 2009 loss reserves:
The Insurance Companies recorded $11.9 million of net prior year unfavorable development for the marine business, of which $10.6 million arose in the marine liability business due to large loss activity in excess of our prior expectations mostly across underwriting years 2005 to 2008 that we recognized by reserve strengthening.
60
The Insurance Companies recorded $35.7 million of net prior year savings for property casualty business in total. The favorable development included:
| • | $36.5 million for contractors' liability due to an actuarial review conducted in 2009 which indicated that loss development on the 2006 and prior underwriting years has been more favorable than our prior expectations for those underwriting years |
| • | $9.3 million from our primary E&S lines and $6.2 million in excess casualty business due to favorable loss trends in underwriting years 2007 and prior, and |
| • | $8.0 million of favorable development on our offshore energy (NavTech) book due to favorable claims trends across a number of prior underwriting years. |
Partially offsetting these favorable developments were adverse development of:
| • | $12.0 million in our Nav Pac business due to reported loss activity in excess of our prior expectations from most underwriting years resulting from reviews of open claims in the auto and liability lines of business |
| • | $6.4 million from our liquor business, which is now in run-off, and |
| • | $5.9 million in our personal umbrella books of business across most underwriting years where large loss activity has exceeded our expectations. |
The Insurance Companies recorded $20.7 million of net prior year unfavorable development for professional liability.
| • | The directors and officers' liability book of business had $12.4 million of adverse development, which was primarily attributable to the unexpected development of previously reported claims in the 2006 and prior underwriting years. This loss activity was inconsistent with the loss emergence trends that we observed in calendar years 2007 and 2008 and it caused us to increase our ultimate loss projections in the 2006 and prior underwriting years, as well as those in the more current underwriting years. |
| • | The lawyers' liability book of business had adverse development of $8.3 million due to reported loss activity in underwriting years 2005 to 2008 in excess of our prior expectations. |
The Lloyd's Operations recorded $5.9 million of net favorable development which included: $11.0 million on Marine business concentrated in the liability specie and cargo books due to reported losses being less than our expectations in underwriting years 2004 to 2008 and $2.5 million on offshore energy business due to favorable loss trends in several years, partially offset by $4.7 million of adverse loss development in the professional liability books due to reported loss activity in excess of our expectations in the lawyers liability book of business for losses occurring in 2007 and $3.0 million in the property book due to an extension in the loss development pattern for the 2006 and 2007 underwriting years.
Following is a discussion of relevant factors impacting our 2008 loss reserves:
The Insurance Companies recorded $5.3 million of net prior year savings for marine business, primarily comprised of $4.7 million of savings in the marine liability business, $2.8 million of savings in the protection and indemnity business, $1.4 million of savings in the transport business and $1.4 million of savings due to a review of reinsurance recoverable in the second quarter of 2008, partially offset by $2.7 million of strengthening in the cargo business, $1.4 million of strengthening in the craft and hull businesses, and $0.7 million recorded for a commutation with a reinsurer. The favorable development for marine liability, protection and indemnity, and transport was primarily due to reduced claims activity for underwriting years 2003 through 2006 as well as IBNR loss reserve reductions that resulted from the reduced claims activity. The adverse development for cargo, craft and hull was primarily due to several large claims in underwriting years 2005 and 2006.
61
The Insurance Companies recorded $33.1 million of net prior year savings for property casualty business. This included $31.6 million savings in the contractors liability business, $3.8 million of savings in the offshore energy business, $3.7 million of net prior year savings in the property and aviation run-off business $1.4 million of savings in the commercial umbrella business, $1.0 million of savings in the personal umbrella business, and $0.8 million of savings in the primary E&S business; partially offset by $1.6 million of net adverse development in the middle markets business as a result of an actuarial analysis that indicated that strengthening is required for the automobile coverage due to frequency and severity in excess of our expectations and $7.1 million of strengthening due to greater than expected loss activity in a discontinued liquor liability program and $0.8 million of strengthening in the program business. The favorable development for contractors' liability, commercial umbrella, personal umbrella and primary E&S were primarily due to reduced claims activity in underwriting years 2003 through 2006. The favorable development for the aviation business was as a result of an actuarial analysis that indicated that the losses are substantially reported and the IBNR loss reserves could be reduced. The adverse development for the liquor liability business was due to a discontinued program and the adverse development on the programs business was due to an active program.
The Insurance Companies recorded $3.6 million of net prior year savings for professional liability. This was primarily due to the reduction in case and IBNR reserves for the directors and officers business in underwriting years 2004 through 2006 resulting from reported losses being less than anticipated during 2008.
The Lloyd's Operations recorded $8.8 million of net prior year savings, primarily in the marine liability, energy, specie and reinsurance business for underwriting years 2005 and prior. The favorable development is the result of more extensive analysis of the potential future development which led us to shorten the development patterns.
Following is a discussion of relevant factors impacting our 2007 loss reserves:
The Insurance Companies recorded $11.6 million of net prior years' savings in the marine business primarily comprised of $6.5 million of savings in the transport business, $3.7 million of savings in the marine liability business, $1.6 million of savings in the cargo business, $1.0 million of savings in each of the hull; partially offset by $1.6 million for uncollectible reinsurance recoverables for asbestos losses. The favorable development for the liability, cargo and hull coverages was primarily due to reduced claim activity for the 2005 and 2006 underwriting years. Prior to 2007, because the Company did not have sufficient experience in the transport product line, it instead used its hull and liability products loss development experience as a key assumption in setting the IBNR loss reserves for its transport product. Commencing in 2007, our actuaries determined that the Company's loss development experience for its transport product had become sufficiently credible to begin establishing transport reserves using such experience, which resulted in the prior year savings referred to above recorded for this business.
62
The Insurance Companies recorded $11.8 million of net prior years' savings almost entirely for its property casualty business related to the contractors' liability business for the years 1998 through 2006. The prior years' savings recorded for contractors' liability business was due mostly to continued favorable loss frequency and severity trends for 2003 to 2006 compared to expectations. Our actuaries believe that the favorable loss frequency trends result primarily from a number of underwriting and coverage changes since 2002, including the migration to non-admitted business from admitted business in 2003, which allowed the Company to exclude certain previously permitted exposures (for example, exposure to construction work performed prior to the policy inception), and withdrawals from certain contractor classes previously underwritten. Our actuaries believe that the favorable loss severity trends result primarily from improved claim practices coupled with a California legislative change, effective in mid-2002, which provides for an alternative dispute resolution system with respect to construction defect claims and is intended to avoid or mitigate costly litigation and claims settlements. While our actuaries were unable to precisely quantify the impact of each of the foregoing factors, such factors were judgmentally taken into account in recording such prior years' savings for contractors' liability business by evaluating actual loss development compared to expected loss development coupled with a frequency and severity claims analysis conducted in 2007.
The Insurance Companies have historically reserved for the professional liability business using ultimate loss ratios based on industry experience for this line of business given the Company's limited claims history. Such industry experience is heavily influenced by the historical frequency and severity of large securities class action lawsuits. During 2007, the Insurance Companies reduced the net reserves for such claims-made policies compared to year-end 2006 by $10.4 million, mostly related to policies issued in 2004 and 2005. The reductions were made to recognize both the low level of open claim counts and the lack of observed claim severity compared to expectations at the time the reserves were initially established using industry experience.
The Lloyd's Operations recorded $13.2 million of net prior year savings, comprised of $3.4 million due to a review of the 2005 Hurricanes Katrina and Rita loss estimates, a release of approximately $2.0 million following a review of open claim files for the years 1998 to 2001, a $4.6 million reduction in our 2004 underwriting year estimates for the marine liability book due to favorable loss trends, and the remaining $3.2 million was mostly for offshore energy and marine liability business on business underwritten during 2002.
Hurricanes Gustav and Ike
During 2008, we recorded gross and net loss estimates of $114.0 million and $17.2 million, respectively, exclusive of $12.2 million for the cost of excess-of-loss reinstatement premiums, related to the third quarter 2008 Hurricanes Gustav and Ike. Our pre-tax net loss as a result of Hurricanes Gustav and Ike was approximately $29.3 million, which increased our 2008 combined ratio by 4.3 ratio points.
63
The following table sets forth our gross and net loss and LAE reserves, incurred loss and LAE, and payments for the 2008 Hurricanes Gustav and Ike for the periods indicated:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||
| ||||||||
Gross of Reinsurance | ||||||||
Beginning gross reserves | $ | 107,399 | $ | - | ||||
Incurred loss & LAE | 1,039 | 114,000 | ||||||
Calendar year payments | 48,929 | 6,601 | ||||||
| ||||||||
Ending gross reserves | $ | 59,509 | $ | 107,399 | ||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
Gross case loss reserves | $ | 34,015 | $ | 70,299 | ||||
Gross IBNR loss reserves | 25,494 | 37,100 | ||||||
| ||||||||
Ending gross reserves | $ | 59,509 | $ | 107,399 | ||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
Net of Reinsurance | ||||||||
Beginning net reserves | $ | 12,923 | $ | - | ||||
Incurred loss & LAE | 978 | 17,169 | ||||||
Calendar year payments | 11,218 | 4,246 | ||||||
| ||||||||
Ending net reserves | $ | 2,683 | $ | 12,923 | ||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
Net case loss reserves | $ | 1,793 | $ | 11,696 | ||||
Net IBNR loss reserves | 890 | 1,227 | ||||||
| ||||||||
Ending net reserves | $ | 2,683 | $ | 12,923 | ||||
| ||||||||
Hurricanes Katrina and Rita
During the 2005 third quarter, we recorded gross and net loss estimates of $471.0 million and $22.3 million, respectively, exclusive of $14.5 million for the cost of excess-of-loss reinstatement premiums, related to Hurricanes Katrina and Rita.
64
The following tables set forth our gross and net loss and LAE reserves, incurred loss and LAE, and payments for the 2005 Hurricanes Katrina and Rita for the periods indicated:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Gross of Reinsurance | ||||||||||||
Beginning gross reserves | $ | 97,732 | $ | 141,831 | $ | 319,230 | ||||||
Incurred loss & LAE | 671 | (12,250 | ) | (29,349 | ) | |||||||
Calendar year payments | 31,365 | 31,849 | 148,050 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Ending gross reserves | $ | 67,038 | $ | 97,732 | $ | 141,831 | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Gross case loss reserves | $ | 49,291 | $ | 62,732 | $ | 94,959 | ||||||
Gross IBNR loss reserves | 17,747 | 35,000 | 46,872 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Ending gross reserves | $ | 67,038 | $ | 97,732 | $ | 141,831 | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net of Reinsurance | ||||||||||||
Beginning net reserves | $ | 3,667 | $ | 4,519 | $ | 10,003 | ||||||
Incurred loss & LAE | 114 | (990 | ) | (1,909 | ) | |||||||
Calendar year payments | 245 | (138 | ) | 3,575 | ||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Ending net reserves | $ | 3,536 | $ | 3,667 | $ | 4,519 | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net case loss reserves | $ | 183 | $ | 279 | $ | 646 | ||||||
Net IBNR loss reserves | 3,353 | 3,388 | 3,873 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Ending net reserves | $ | 3,536 | $ | 3,667 | $ | 4,519 | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
Asbestos Liability
Our exposure to asbestos liability principally stems from marine liability insurance written on an occurrence basis during the mid-1980s. In general, our participation on such risks is in the excess layers, which requires the underlying coverage to be exhausted prior to coverage being triggered in our layer. In many instances we are one of many insurers who participate in the defense and ultimate settlement of these claims, and we are generally a minor participant in the overall insurance coverage and settlement.
The reserves for asbestos exposures at December 31, 2009 are for: (i) one large settled claim for excess insurance policy limits exposed to a class action suit against an insured involved in the manufacturing or distribution of asbestos products being paid over several years (two other large settled claims were fully paid in 2007); (ii) other insureds not directly involved in the manufacturing or distribution of asbestos products, but that have more than incidental asbestos exposure for their purchase or use of products that contained asbestos; and (iii) attritional asbestos claims that could be expected to occur over time. Substantially all of our asbestos liability reserves are included in our marine loss reserves.
We believe that there are no remaining known claims where we would suffer a material loss as a result of excess policy limits being exposed to class action suits for insureds involved in the manufacturing or distribution of asbestos products. There can be no assurances, however, that material loss development may not arise in the future from existing asbestos claims or new claims given the evolving and complex legal environment that may directly impact the outcome of the asbestos exposures of our insureds.
65
The following tables set forth our gross and net loss and LAE reserves for our asbestos exposures for the periods indicated:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Gross of Reinsurance | ||||||||||||
Beginning gross reserves | $ | 21,774 | $ | 23,194 | $ | 37,171 | ||||||
Incurred loss & LAE | 928 | 796 | (780 | ) | ||||||||
Calendar year payments | 555 | 2,216 | 13,197 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Ending gross reserves | $ | 22,147 | $ | 21,774 | $ | 23,194 | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Gross case loss reserves | $ | 14,291 | $ | 13,918 | $ | 16,014 | ||||||
Gross IBNR loss reserves | 7,856 | 7,856 | 7,180 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Ending gross reserves | $ | 22,147 | $ | 21,774 | $ | 23,194 | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net of Reinsurance | ||||||||||||
Beginning net reserves | $ | 16,683 | $ | 16,717 | $ | 21,381 | ||||||
Incurred loss & LAE | (25 | ) | 263 | 1,779 | ||||||||
Calendar year payments | (105 | ) | 297 | 6,443 | ||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Ending net reserves | $ | 16,763 | $ | 16,683 | $ | 16,717 | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net case loss reserves | $ | 9,112 | $ | 9,032 | $ | 9,715 | ||||||
Net IBNR loss reserves | 7,651 | 7,651 | 7,002 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Ending net reserves | $ | 16,763 | $ | 16,683 | $ | 16,717 | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
The ceded asbestos paid and unpaid recoverables were $8.9 million at December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. During 2007, we increased our provision for uncollectible reinsurance for asbestos losses by $1.6 million which was recorded in incurred losses. In addition, in 2007, we settled demands for arbitration with two asbestos reinsurers. We believe that we will be able to collect reinsurance on the gross portion of its historic gross asbestos exposure in the above table. To the extent we incur additional gross loss development for our historic asbestos exposure, we do not expect to realize additional reinsurance recoverables.
66
Loss Reserves
As illustrated in the following table, our overall reinsurance recoverable amounts for paid and unpaid losses have decreased during 2009 as we utilized less reinsurance in 2009 compared to 2008:
| December 31, | December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | Change | ||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Reinsurance recoverables: | ||||||||||||
Paid losses | $ | 76,505 | $ | 67,227 | $ | 9,278 | ||||||
Unpaid losses and LAE reserves | 807,352 | 853,793 | (46,441 | ) | ||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Total | $ | 883,857 | $ | 921,020 | $ | (37,163 | ) | |||||
| ||||||||||||
The following table sets forth our gross reserves for losses and LAE reduced for reinsurance recoverable on such amounts resulting in net loss and LAE reserves (a non-GAAP measure reconciled in the following table) for the periods indicated:
| December 31, | December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | Change | ||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Gross reserves for losses and LAE | $ | 1,920,286 | $ | 1,853,664 | $ | 66,622 | ||||||
Less: Reinsurance recoverable on unpaid losses and LAE reserves | 807,352 | 853,793 | (46,441 | ) | ||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net loss and LAE reserves | $ | 1,112,934 | $ | 999,871 | $ | 113,063 | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
67
The following tables set forth our net case loss and LAE reserves and net IBNR reserves (a non-GAAP measure reconciled above) by segment and line of business for the periods indicated:
| December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net | Net | Total | % of IBNR | |||||||||||||
| Reported | IBNR | Net Loss | to Total Net | |||||||||||||
| Reserves | Reserves | Reserves | Loss Reserves | |||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Insurance Companies: | ||||||||||||||||
Marine | $ | 113,604 | $ | 100,042 | $ | 213,646 | 46.8 | % | ||||||||
Property Casualty | 134,427 | 351,985 | 486,412 | 72.4 | % | |||||||||||
Professional liability | 38,410 | 68,807 | 107,217 | 64.2 | % | |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Total Insurance Companies | 286,441 | 520,834 | 807,275 | 64.5 | % | |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Lloyd's Operations: | ||||||||||||||||
Marine | 107,800 | 101,851 | 209,651 | 48.6 | % | |||||||||||
Property Casualty | 27,148 | 25,175 | 52,323 | 48.1 | % | |||||||||||
Professional liability | 7,442 | 36,243 | 43,685 | 83.0 | % | |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Total Lloyd's Operations | 142,390 | 163,269 | 305,659 | 53.4 | % | |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 428,831 | $ | 684,103 | $ | 1,112,934 | 61.5 | % | ||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2008 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net | Net | Total | % of IBNR | |||||||||||||
| Reported | IBNR | Net Loss | to Total Net | |||||||||||||
| Reserves | Reserves | Reserves | Loss Reserves | |||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
Insurance Companies: | ||||||||||||||||
Marine | $ | 96,244 | $ | 96,995 | $ | 193,239 | 50.2 | % | ||||||||
Property Casualty | 115,810 | 358,305 | 474,115 | 75.6 | % | |||||||||||
Professional liability | 22,913 | 58,793 | 81,706 | 72.0 | % | |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Total Insurance Companies | 234,967 | 514,093 | 749,060 | 68.6 | % | |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Lloyd's Operations: | ||||||||||||||||
Marine | 99,233 | 78,293 | 177,526 | 44.1 | % | |||||||||||
Property Casualty | 26,218 | 16,386 | 42,604 | 38.5 | % | |||||||||||
Professional liability | 5,822 | 24,859 | 30,681 | 81.0 | % | |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Total Lloyd's Operations | 131,273 | 119,538 | 250,811 | 47.7 | % | |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 366,240 | $ | 633,631 | $ | 999,871 | 63.4 | % | ||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
68
At December 31, 2009, the IBNR loss reserve was $684.1 million or 61.5% of our total loss reserves compared to $633.6 million or 63.4% in 2008.
The increase in net loss reserves in all active lines of business is generally a reflection of the growth in net premium volume over the last three years coupled with a changing mix of business to longer tail lines of business such as the specialty lines of business (construction defect, commercial excess, primary excess), professional liability lines of business and marine liability and transport business in ocean marine. These products, which typically have a longer settlement period compared to the mix of business we have historically written, are becoming larger components of our overall business.
Commission Expense. Commission expenses paid to unaffiliated brokers and agents are generally based on a percentage of the gross written premiums and are reduced by ceding commissions we may receive on the ceded written premiums. Commissions are generally deferred and recorded as deferred policy acquisition costs to the extent that they relate to unearned premium. The percentages of commission expenses to net earned premium was 14.5% in 2009, 13.9% in 2008 and 12.9% in 2007. The 2008 commission expense ratio excluding the effects of the 2008 Hurricanes was 13.7%.
Other Operating Expense. The 7.7% and 11.5% increases in other operating expenses when comparing 2009 to 2008 and comparing 2008 to 2007, respectively, were attributable primarily to employee related expenses resulting from expansion of the business.
Interest Expense. The interest expense reflects interest on our Senior notes issued in April 2006.
Income Taxes
The income tax expense was $23.7 million, $17.0 million and $43.6 million for 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively. The effective tax rates for 2009, 2008 and 2007 were 27.3%, 24.8% and 31.3%, respectively. Our effective tax rate was less than 35% due to permanent differences between book and tax return income, with the most significant item being tax exempt interest. As of December 31, 2009 and 2008, the net deferred federal, foreign, state and local tax assets were $31.2 million and $54.7 million, respectively.
We are subject to the tax regulations of the United States and foreign countries in which we operate. We file a consolidated federal tax return, which includes all domestic subsidiaries and the U.K. Branch. The income from the foreign operations is designated as either U.S. connected income or non-U.S. connected income. Lloyd's is required to pay U.S. income tax on U.S. connected income written by Lloyd's syndicates. Lloyd's and the IRS have entered into an agreement whereby the amount of tax due on U.S. connected income is calculated by Lloyd's and remitted directly to the IRS. These amounts are then charged to the corporate members in proportion to their participation in the relevant syndicates. Our corporate members are subject to this agreement and will receive U.K. tax credits for any U.S. income tax incurred up to the U.K. income tax charged on the U.S. income. The non-U.S. connected insurance income would generally constitute taxable income under the Subpart F income section of the Internal Revenue Code since less than 50% of our premium is derived within the U.K. and would therefore be subject to U.S. taxation when the Lloyd's year of account closes. Taxes are accrued at a 35% rate on our foreign source insurance income and foreign tax credits, where available, are utilized to offset U.S. tax as permitted. Our effective tax rate for Syndicate 1221 taxable income could substantially exceed 35% to the extent we are unable to offset U.S. taxes paid under Subpart F tax regulations with U.K. tax credits on future underwriting year distributions. U.S. taxes are not accrued on the earnings of our foreign agencies as these earnings are not subject to the Subpart F tax regulations. These earnings are subject to taxes under U.K. tax regulations. A finance bill was enacted in the U.K. on July 19, 2007 that reduces the U.K. corporate tax rate from 30% to 28% effective April 1, 2008. The effect of such tax rate change was not material to our financial statements.
We have not provided for U.S. deferred income taxes on the undistributed earnings of approximately $57.6 million of our non-U.S. subsidiaries since these earnings are intended to be permanently reinvested in the foreign subsidiary. However, in the future, if such earnings were distributed to the Company, taxes of approximately $4.0 million would be payable on such undistributed earnings and would be reflected in the tax provision for the year in which these earnings are no longer intended to be permanently reinvested in the non-U.S. subsidiary assuming all foreign tax credits are realized.
69
We had net state and local deferred tax assets amounting to potential future tax benefits of $2.6 million and $6.2 million at December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. Included in the deferred tax assets are net operating loss carryforwards of $1.3 million and $0.5 million at December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. A valuation allowance was established for the full amount of these potential future tax benefits due to the uncertainty associated with their realization. Our state and local tax carryforwards at December 31, 2009 expire from 2023 to 2025.
Segment Information
We classify our business into two underwriting segments consisting of the Insurance Companies and the Lloyd's Operations, which are separately managed, and a Corporate segment. Segment data for each of the two underwriting segments include allocations of revenues and expenses of the wholly-owned underwriting management companies and the Parent Company's operating expenses and related income tax amounts. The Corporate segment consists of the Parent Company's investment income, interest expense and the related tax effect.
We evaluate the performance of each segment based on its underwriting and GAAP results. The Insurance Companies' and the Lloyd's Operations' results are measured by taking into account net earned premiums, net losses and loss adjustment expenses, commission expenses, other operating expenses, commission income and other income (expense). Each segment also maintains its own investments, on which it earns income and realizes capital gains or losses. Our underwriting performance is evaluated separately from the performance of our investment portfolios.
Following are the financial results of our two underwriting segments.
Insurance Companies
The Insurance Companies consist of Navigators Insurance Company, including its U.K. Branch, and its wholly-owned subsidiary, Navigators Specialty Insurance Company. They are primarily engaged in underwriting marine insurance and related lines of business, professional liability insurance and specialty lines of business including contractors general liability insurance, commercial umbrella and primary and excess casualty businesses. Navigators Specialty Insurance Company underwrites specialty and professional liability insurance on an excess and surplus lines basis. Navigators Specialty Insurance Company is 100% reinsured by Navigators Insurance Company.
70
The following table sets forth the results of operations for the Insurance Companies for the periods indicated:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Gross written premiums | $ | 730,776 | $ | 762,190 | $ | 774,346 | ||||||
Net written premiums | 477,673 | 472,688 | 478,018 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net earned premiums | 479,121 | 463,298 | 443,456 | |||||||||
Net losses and loss adjustment expenses | (304,672 | ) | (275,767 | ) | (256,652 | ) | ||||||
Commission expenses | (61,949 | ) | (55,752 | ) | (52,490 | ) | ||||||
Other operating expenses | (104,801 | ) | (92,297 | ) | (81,053 | ) | ||||||
Commission income and other income (expense) | 3,498 | 2,145 | 1,510 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Underwriting profit | 11,197 | 41,627 | 54,771 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net investment income | 65,717 | 63,544 | 58,261 | |||||||||
Net realized gains (losses) | 533 | (37,822 | ) | 1,973 | ||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Income before income tax expense | 77,447 | 67,349 | 115,005 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Income tax expense | 19,819 | 16,401 | 35,061 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 57,628 | $ | 50,948 | $ | 79,944 | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Identifiable assets | $ | 2,554,037 | $ | 2,477,139 | $ | 2,322,647 | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Loss and loss expenses ratio | 63.6 | % | 59.5 | % | 57.9 | % | ||||||
Commission expense ratio | 12.9 | % | 12.0 | % | 11.8 | % | ||||||
Other operating expenses ratio (1) | 21.1 | % | 19.5 | % | 17.9 | % | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
Combined ratio | 97.6 | % | 91.0 | % | 87.6 | % | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
| (1) | Includes Other operating expenses and Commission income and Other income (expense). |
71
The following table sets forth the underwriting results for the Insurance Companies for the periods indicated:
| Year Ended December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net | Losses | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Earned | and LAE | Underwriting | Underwriting | Loss | Expense | Combined | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Premiums | Incurred | Expenses | Profit (Loss) | Ratio | Ratio | Ratio | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Marine | $ | 157,534 | $ | 109,916 | $ | 50,451 | $ | (2,833 | ) | 69.8 | % | 32.0 | % | 101.8 | % | |||||||||||||
Property Casualty | 246,143 | 123,775 | 86,116 | 36,252 | 50.3 | % | 35.0 | % | 85.3 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Professional Liability | 75,444 | 70,981 | 26,685 | (22,222 | ) | 94.1 | % | 35.4 | % | 129.5 | % | |||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 479,121 | $ | 304,672 | $ | 163,252 | $ | 11,197 | 63.6 | % | 34.0 | % | 97.6 | % | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended December 31, 2008 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net | Losses | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Earned | and LAE | Underwriting | Underwriting | Loss | Expense | Combined | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Premiums | Incurred | Expenses | Profit (Loss) | Ratio | Ratio | Ratio | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Marine | $ | 132,005 | $ | 84,099 | $ | 38,184 | $ | 9,722 | 63.7 | % | 28.9 | % | 92.6 | % | ||||||||||||||
Property Casualty | 273,977 | 158,457 | 87,310 | 28,210 | 57.8 | % | 31.9 | % | 89.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Professional Liability | 57,316 | 33,211 | 20,410 | 3,695 | 57.9 | % | 35.6 | % | 93.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 463,298 | $ | 275,767 | $ | 145,904 | $ | 41,627 | 59.5 | % | 31.5 | % | 91.0 | % | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended December 31, 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net | Losses | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Earned | and LAE | Underwriting | Underwriting | Loss | Expense | Combined | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Premiums | Incurred | Expenses | Profit (Loss) | Ratio | Ratio | Ratio | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Marine | $ | 112,370 | $ | 64,802 | $ | 31,878 | $ | 15,690 | 57.7 | % | 28.4 | % | 86.1 | % | ||||||||||||||
Property Casualty | 275,937 | 159,248 | 80,509 | 36,180 | 57.7 | % | 29.2 | % | 86.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Professional Liability | 55,149 | 32,602 | 19,646 | 2,901 | 59.1 | % | 35.6 | % | 94.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 443,456 | $ | 256,652 | $ | 132,033 | $ | 54,771 | 57.9 | % | 29.7 | % | 87.6 | % | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Overall, the net earned premium increased 3.4%, 4.5% and 34.5% in 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively, reflecting overall increased retention of the business written, higher average renewal rates in 2009 overall business expansion in 2007 and expansion of our professional liability business. These factors were partially offset by a decline in our property casualty business in 2009 as well as overall average renewal rate declines in 2008.
The 2009 underwriting results were favorably impacted by $3.1 million or 0.6 loss ratio points for net prior year savings, which is discussed in the prior year reserve redundancies/deficiencies section. The 2009 net prior year savings declined $38.8 million compared to 2008.
72
The following table sets forth the impact of Hurricanes Gustav and Ike on the Insurance Companies' 2008 financial results:
| Hurricane | Hurricane | |||||||||||
| Gustav | Ike | Total | ||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Reduction in net earned premiums for reinstatement costs | $ | (871 | ) | $ | (6,343 | ) | $ | (7,214 | ) | |||
Gross losses incurred | 7,200 | 53,800 | 61,000 | |||||||||
Reinsurance recoverable | 4,377 | 47,546 | 51,923 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net losses incurred | 2,823 | 6,254 | 9,077 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Underwriting loss | $ | (3,694 | ) | $ | (12,597 | ) | $ | (16,291 | ) | |||
| ||||||||||||
After-tax net loss | $ | (2,401 | ) | $ | (8,188 | ) | $ | (10,589 | ) | |||
| ||||||||||||
Reduction in earnings per share | $ | (0.14 | ) | $ | (0.48 | ) | $ | (0.62 | ) | |||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Effect on combined ratio: | ||||||||||||
Loss and LAE ratio | 0.7 | % | 2.1 | % | 2.8 | % | ||||||
Expense ratio | 0.1 | % | 0.4 | % | 0.5 | % | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
Combined ratio | 0.8 | % | 2.5 | % | 3.3 | % | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
The 2008 underwriting results were favorably impacted by $41.9 million or 9.0 loss ratio points for net prior year savings, which is discussed in the prior year reserve redundancies/deficiencies section. The 2008 pre-tax net loss to the Insurance Companies as the result of losses caused by Hurricanes Gustav and Ike of approximately $16.3 million, including $7.2 million of reinstatement costs, increased the Insurance Companies 2008 combined ratio by 10.1 combined ratio points. The after-tax effect reduced net income by $10.6 million.
The 2007 underwriting results were favorably impacted by approximately $33.8 million or 7.6 loss ratio points for net prior year savings across all of our lines of business due to favorable loss development trends.
Reviews of our Insurance Companies Hurricanes Katrina and Rita exposures during 2007 resulted in a reduction to the Insurance Companies pre-tax income by $1.5 million. Much of this impact was the result of reallocating our net retention for these events between our Insurance Companies and Lloyd's Operations.
The approximate annualized pre-tax yields on the Insurance Companies' investment portfolio, excluding net realized capital gains and losses, approximated 4.1%, 4.3% and 4.5% for 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively. The increase in net investment income in 2009, 2008 and 2007 versus the comparable prior year was primarily due to the investment of new funds from positive cash flow from operations. The portfolio's duration was 4.7 years at December 31, 2009 and 4.8 years at December 31, 2008.
The 2009 and 2008 results included provisions of $10.2 million and $36.4 million, respectively, for declines in the market value of securities which were considered to be other-than-temporary. The after-tax effects of such provisions on the 2009 and 2008 net income were $6.7 million and $23.7 million, respectively.
73
Lloyd's Operations
The Lloyd's Operations primarily underwrite marine and related lines of business along with professional liability insurance, and construction coverages for onshore energy business at Lloyd's through Syndicate 1221. The European property business, written by the Lloyd's Operations and the U.K. Branch beginning in 2006, was discontinued in the 2008 second quarter. Our Lloyd's Operations includes NUAL, a Lloyd's underwriting agency which manages Syndicate 1221.
Syndicate 1221's stamp capacity was £124 million ($194 million) in 2009, £123 million ($228 million) in 2008 and £140 million ($280 million) in 2007. Stamp capacity is a measure of the amount of premium a Lloyd's syndicate is authorized to write as determined by the Council of Lloyd's. We controlled 100% of Syndicate 1221's total stamp capacity in 2009, 2008 and 2007 through our wholly-owned Lloyd's corporate member (we utilized two wholly-owned Lloyd's corporate members prior to the 2008 underwriting year). Syndicate 1221's stamp capacity is expressed net of commission (as is standard at Lloyd's). The Syndicate 1221 premium recorded in our financial statements is gross of commission. We provide letters of credit to Lloyd's to support our participation in Syndicate 1221's stamp capacity as discussed below under the caption Liquidity and Capital Resources .
74
The following table sets forth the results of operations of the Lloyd's Operations for the following periods:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Gross written premiums | $ | 314,142 | $ | 322,732 | $ | 296,361 | ||||||
Net written premiums | 223,582 | 188,927 | 167,778 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net earned premiums | 204,242 | 180,678 | 158,521 | |||||||||
Net losses and loss adjustment expenses | (131,326 | ) | (117,364 | ) | (83,940 | ) | ||||||
Commission expenses | (37,727 | ) | (34,033 | ) | (25,123 | ) | ||||||
Other operating expenses | (27,896 | ) | (30,961 | ) | (29,356 | ) | ||||||
Commission income and other income (expense) | 961 | (600 | ) | 504 | ||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Underwriting profit (loss) | 8,254 | (2,280 | ) | 20,606 | ||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net investment income | 9,229 | 11,655 | 10,524 | |||||||||
Net realized gains (losses) | (3,193 | ) | (477 | ) | 33 | |||||||
| ||||||||||||
Income before income tax expense | 14,290 | 8,898 | 31,163 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Income tax expense | 5,582 | 3,269 | 10,946 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 8,708 | $ | 5,629 | $ | 20,217 | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Identifiable assets | $ | 799,577 | $ | 779,800 | $ | 744,002 | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Loss and loss expenses ratio | 64.3 | % | 65.0 | % | 53.0 | % | ||||||
Commission expense ratio | 18.5 | % | 18.8 | % | 15.8 | % | ||||||
Other operating expenses ratio (1) | 13.2 | % | 17.5 | % | 18.2 | % | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
Combined ratio | 96.0 | % | 101.3 | % | 87.0 | % | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
| (1) | Includes Other operating expenses and Commission income and Other income (expense). |
The 2009 earnings in the Lloyd's Operations improved $3.1 million compared to 2008. The Lloyd's Operations utilized less reinsurance in 2009 compared to 2008, resulting in higher net premiums. In addition, 2008 results were impacted by losses caused by Hurricanes Gustav and Ike of approximately $13.1 million, including $5.0 million of reinstatement costs, which increased the 2008 combined ratio by 7.1 combined ratio points and reduced net income by $8.5 million.
The 2009 underwriting results were favorably impacted by approximately $5.9 million or 2.9 loss ratio points for net prior years' savings due to favorable loss development trends which are discussed in the prior year reserve redundancies/deficiencies section. The 2009 net prior years' savings was a decline of $3.0 million compared to 2008.
75
The following table sets forth the impact of Hurricanes Gustav and Ike on the Lloyd's Operations 2008 financial results:
| Hurricane | Hurricane | |||||||||||
| Gustav | Ike | Total | ||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Reduction in net earned premiums for reinstatement costs | $ | (672 | ) | $ | (4,292 | ) | $ | (4,964 | ) | |||
Gross losses incurred | 6,800 | 46,200 | 53,000 | |||||||||
Reinsurance recoverable | 4,623 | 40,285 | 44,908 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Net losses incurred | 2,177 | 5,915 | 8,092 | |||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Underwriting loss | $ | (2,849 | ) | $ | (10,207 | ) | $ | (13,056 | ) | |||
| ||||||||||||
After-tax net loss | $ | (1,852 | ) | $ | (6,635 | ) | $ | (8,487 | ) | |||
| ||||||||||||
Reduction in earnings per share | $ | (0.11 | ) | $ | (0.39 | ) | $ | (0.50 | ) | |||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Effect on combined ratio: | ||||||||||||
Loss and LAE ratio | 1.4 | % | 4.7 | % | 6.1 | % | ||||||
Expense ratio | 0.2 | % | 0.8 | % | 1.0 | % | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
Combined ratio | 1.6 | % | 5.5 | % | 7.1 | % | ||||||
| ||||||||||||
The 2008 earnings in the Lloyd's Operations were impacted by losses caused by Hurricanes Gustav and Ike of approximately $13.1 million, including $5.0 million of reinstatement costs, which increased the 2008 combined ratio by 7.1 combined ratio points. The after tax effect reduced net income by $8.5 million.
The 2008 underwriting results were favorably impacted by approximately $8.8 million or 4.9 loss ratio points for net prior years' savings due to favorable loss development trends, primarily in the liability and offshore energy lines in underwriting years 2006 and prior, which is discussed in the prior year reserve redundancies/deficiencies section. The 2007 earnings in the Lloyd's Operations reflect the continued favorable loss development trends.
The 2007 underwriting results were favorably impacted by approximately $13.2 million or 8.3 loss ratio points for net prior years' savings due to favorable loss development trends, primarily in our 2004 and 2005 underwriting years.
Reviews of our Lloyd's Operations' Hurricanes Katrina and Rita exposures during 2007 resulted in a reduction to the storm loss estimates and increased pre-tax income by $4.1 million consisting of $3.4 million of decreases to incurred losses and a $0.7 million reduction in our reinstatement cost estimates. A portion of this impact was the result of reallocating our net retention for these events between our Insurance Companies and Lloyd's Operations.
The pre-tax yields on the Lloyd's Operations investments, excluding net realized capital gains and losses, approximated 2.7%, 3.4% and 3.9% for 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively. Such yields are net of interest credits to certain reinsurers for funds withheld by our Lloyd's Operations. Generally, the Lloyd's Operations' investments have been invested with a relatively short average duration, which is reflected in the yield, in order to meet liquidity needs. The decrease in the Lloyd's Operations' net investment income in 2009 was due to lower investment yields. The increase in the Lloyd's Operations' net investment income in 2008 and 2007 is reflective of the increased investment portfolio primarily due to positive cash flow from operations. The average duration of the Lloyd's Operations' investment portfolio was 1.6 years at December 31, 2009 compared to 1.4 years at December 31, 2008.
The 2009 and 2008 results included provisions of $1.6 million and $0.7 million, respectively, for declines in the market value of securities which were considered to be other-than-temporary. The after-tax effects of such provisions on the 2009 and 2008 net income were $1.2 million and $0.5 million, respectively.
76
See "Results of Operations and Overview - Income Taxes" for a discussion of the Lloyd's Operations' income taxes, included herein.
Off-Balance Sheet Transactions
We have no material off-balance sheet transactions with the exception of our letter of credit facility. For a discussion of our letter of credit facility, see "- Liquidity and Capital Resources", included herein.
Tabular Disclosure of Contractual Obligations
The following table sets forth the best estimate of our known contractual obligations with respect to the items indicated at December 31, 2009:
| Payments Due by Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Less than | More than | |||||||||||||||||||
| Contractual Obligations | Total | 1 Year | 1-3 Years | 3-5 Years | 5 Years | |||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Reserves for losses and LAE (1) | $ | 1,920,286 | $ | 731,746 | $ | 668,866 | $ | 267,634 | $ | 252,040 | ||||||||||
7% Senior Notes (2) | 167,325 | 8,050 | 16,100 | 16,100 | 127,075 | |||||||||||||||
Operating Leases | 54,757 | 7,379 | 15,403 | 13,549 | 18,426 | |||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 2,142,368 | $ | 747,175 | $ | 700,369 | $ | 297,283 | $ | 397,541 | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | The amounts determined are estimates which are subject to a high degree of variation and uncertainty, and are not subject to any specific payment schedule since the timing of these obligations are not set contractually. The amounts in the above table exclude reinsurance recoveries of $807 million. See "Business - Loss Reserves" included herein. | |
| (2) | Includes interest payments. |
77
Investments
The following tables set forth our cash and investments as of December 31, 2009 and 2008. The table as of December 31, 2009 includes other-than-temporarily impaired ("OTTI") securities recognized within other comprehensive income ("OCI").
| Gross | Gross | OTTI | ||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized | Unrealized | Cost or | Recognized | |||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2009 | Fair Value | Gains | (Losses) | Amortized Cost | in OCI | |||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
U.S. Government Treasury bonds, agency bonds and foreign government bonds | $ | 471,598 | $ | 7,397 | $ | (597 | ) | $ | 464,798 | $ | - | |||||||||
States, municipalities and political subdivisions | 676,699 | 25,044 | (2,917 | ) | 654,572 | - | ||||||||||||||
Mortgage- and asset-backed securities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Agency mortgage-backed securities | 283,578 | 12,607 | (98 | ) | 271,069 | - | ||||||||||||||
Residential mortgage obligations | 31,071 | - | (7,246 | ) | 38,317 | (5,723 | ) | |||||||||||||
Asset-backed securities | 16,469 | 612 | (34 | ) | 15,891 | (23 | ) | |||||||||||||
Commercial mortgage-backed securities | 100,393 | 594 | (5,028 | ) | 104,827 | - | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Subtotal | 431,511 | 13,813 | (12,406 | ) | 430,104 | (5,746 | ) | |||||||||||||
Corporate bonds | 236,861 | 9,111 | (759 | ) | 228,509 | - | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Total fixed maturities | 1,816,669 | 55,365 | (16,679 | ) | 1,777,983 | (5,746 | ) | |||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Equity securities - common stocks | 62,610 | 15,244 | (10 | ) | 47,376 | - | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Cash | 509 | - | - | 509 | - | |||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Short-term investments | 176,799 | - | - | 176,799 | - | |||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 2,056,587 | $ | 70,609 | $ | (16,689 | ) | $ | 2,002,667 | $ | (5,746 | ) | ||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
78
| Gross | Gross | |||||||||||||||
| Unrealized | Unrealized | Cost or | ||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2008 | Fair Value | Gains | (Losses) | Amortized Cost | ||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
U.S. Government Treasury bonds, agency bonds and foreign government bonds | $ | 361,656 | $ | 25,741 | $ | (145 | ) | $ | 336,060 | |||||||
States, municipalities and political subdivisions | 614,609 | 12,568 | (8,036 | ) | 610,077 | |||||||||||
Mortgage- and asset-backed securities: | ||||||||||||||||
Agency mortgage-backed securities | 299,775 | 10,930 | (26 | ) | 288,871 | |||||||||||
Residential mortgage obligations | 56,743 | - | (27,119 | ) | 83,862 | |||||||||||
Asset-backed securities | 29,436 | 5 | (1,289 | ) | 30,720 | |||||||||||
Commercial mortgage-backed securities | 92,684 | - | (20,350 | ) | 113,034 | |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Subtotal | 478,638 | 10,935 | (48,784 | ) | 516,487 | |||||||||||
Corporate bonds | 188,869 | 1,398 | (14,660 | ) | 202,131 | |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Total fixed maturities | 1,643,772 | 50,642 | (71,625 | ) | 1,664,755 | |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Equity securities - common stocks | 51,802 | 1,266 | (1,987 | ) | 52,523 | |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Cash | 1,457 | - | - | 1,457 | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Short-term investments | 220,684 | - | - | 220,684 | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 1,917,715 | $ | 51,908 | $ | (73,612 | ) | $ | 1,939,419 | |||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Invested assets increased in 2009 compared to 2008 primarily due to cash flows from operations as well as unrealized gains in 2009. Invested assets increased in 2008 compared to 2007 primarily due to positive cash flows from operations partially offset by unrealized losses in 2008. The consolidated average investment yield of the portfolio decreased in 2009 to 3.8% from 4.1% due to the general decline in market yields over the period. The portfolio's duration was 4.2 years and 4.3 years as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. Since the beginning of 2009, the tax-exempt portion of our investment portfolio has increased by $30.1 million to approximately 34.9% of the fixed maturities investment portfolio at December 31, 2009 compared to approximately 36.8% at December 31, 2008.
We are a specialty insurance company and periods of moderate economic recession or inflation tend not to have a significant direct effect on our underwriting operations. They do, however, impact our investment portfolio. A decrease in interest rates will tend to decrease our yield and have a positive effect on the fair value of our invested assets. An increase in interest rates will tend to increase our yield and have a negative effect on the fair value of our invested assets.
79
Prepayment assumptions associated with the mortgage-backed and asset-backed securities are reviewed on a periodic basis. When changes in prepayment assumptions are deemed necessary as the result of actual prepayments differing from anticipated prepayments, securities are revalued based upon the new prepayment assumptions utilizing the retrospective accounting method.
All fixed maturities, short-term investments and equity securities are carried at fair value. All prices for our fixed maturities, short-term investments and equity securities valued as Level 1 or Level 2 in the fair value hierarchy, as defined in the Financial Accounts Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification 820 ("ASC 820"), Fair Value Measurements , are received from independent pricing services utilized by one of our outside investment managers whom we employ to assist us with investment accounting services. This manager utilizes a pricing committee which approves the use of one or more independent pricing service vendors. The pricing committee consists of five or more members, one from senior management and one from the accounting group with the remainder from the asset class specialists and client strategists. The pricing source of each security is determined in accordance with the pricing source procedures approved by the pricing committee. The investment manager uses supporting documentation received from the independent pricing service vendor detailing the inputs, models and processes used in the independent pricing service vendors' evaluation process to determine the appropriate fair value hierarchy. Any pricing where the input is based solely on a broker price is deemed to be a Level 3 price.
Management has reviewed this process by which the manager determines the prices and has obtained alternative pricing to validate a sampling of the pricing and assess their reasonableness.
80
The following table presents, for each of the fair value hierarchy levels, our fixed maturities, equity securities and short-term investments that are measured at fair value as of December 31, 2009:
| Quoted Prices | Significant | |||||||||||||||
| In Active | Other | Significant | ||||||||||||||
| Markets for | Observable | Unobservable | ||||||||||||||
| Identical Assets | Inputs | Inputs | ||||||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Fixed maturities | $ | 331,925 | $ | 1,484,744 | $ | - | $ | 1,816,669 | ||||||||
Equity securities | 62,610 | - | - | 62,610 | ||||||||||||
Short-term investments | 9,992 | 166,807 | - | 176,799 | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 404,527 | $ | 1,651,551 | $ | - | $ | 2,056,078 | ||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
There were no significant judgments made in classifying instruments in the fair value hierarchy.
The following table presents a reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances for all investments measured at fair value using Level 3 inputs during the twelve months ended December 31, 2009:
| Twelve Months Ended | ||||
| ($ in thousands) | December 31, 2009 | |||
| ||||
Level 3 investments as of January 1 | $ | 156 | ||
Unrealized net gains included in other comprehensive income (loss) | 23 | |||
Purchases, sales, paydowns and amortization | (23 | ) | ||
Transfer from Level 3 | (156 | ) | ||
Transfer to Level 3 | - | |||
| ||||
Level 3 investments as of December 31 | $ | - | ||
| ||||
81
The following tables set forth our U.S. Treasury bonds, agency bonds and foreign government bonds as of December 31, 2009 and 2008:
| Gross | Gross | Cost or | ||||||||||||||
| Fair | Unrealized | Unrealized | Amortized | |||||||||||||
| December 31, 2009 | Value | Gains | (Losses) | Cost | ||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury bonds | $ | 362,614 | $ | 5,549 | $ | (560 | ) | $ | 357,625 | |||||||
Agency bonds | 82,739 | 1,489 | - | 81,250 | ||||||||||||
Foreign government bonds | 26,245 | 359 | (37 | ) | 25,923 | |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 471,598 | $ | 7,397 | $ | (597 | ) | $ | 464,798 | |||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Gross | Gross | Cost or | ||||||||||||||
| Fair | Unrealized | Unrealized | Amortized | |||||||||||||
| December 31, 2008 | Value | Gains | (Losses) | Cost | ||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury bonds | $ | 290,059 | $ | 23,243 | $ | (143 | ) | $ | 266,959 | |||||||
Agency bonds | 58,401 | 2,008 | (2 | ) | 56,395 | |||||||||||
Foreign government bonds | 13,196 | 490 | - | 12,706 | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 361,656 | $ | 25,741 | $ | (145 | ) | $ | 336,060 | |||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
82
The following table sets forth the fifteen largest holdings categorized as state, municipalities and political subdivisions by counterparty as of December 31, 2009:
